Campylobacter Infection: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment


Escrito y verificado por el nutricionista Saúl Sánchez
Campylobacter infection can be contracted from the consumption of contaminated food, and poultry meat is the most likely to contain this type of microorganism.
This pathology develops digestive-type symptoms and can also cause fever. However, some people can overcome it without any symptoms. Be that as it may, it’s still necessary to implement a series of food hygiene mechanisms to prevent potential risks.
Infectious pathologies caused by the consumption of food in poor condition or incorrectly handled are especially dangerous in the case of risk groups. Older people or pregnant women could experience many complications, as well are those who are immunosuppressed for different reasons. In these cases, it’s important to implement good prevention methods.
What are the symptoms of Campylobacter infection?
Normally, the typical symptoms of Campylobacter infection, according to a study published in the Clinics in Laboratory Medicine journal, are the following:
- Diarrhea, sometimes with blood
- Cramps
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
If these symptoms develop, it’s advisable to visit a doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and to implement a series of strategies to speed up healing. Sometimes the use of drugs will be necessary.
Other times it will be necessary to adjust the diet to prevent dehydration and malnutrition problems. In the most serious cases, antibiotics could even be administered to eliminate the infection.
It must be taken into account that, in the most severe cases of Campylobacter infection, reactive arthritis could develop. This is evidenced by research published in the journal Infectious Disease Clinics of North America.
In these cases, it would be absolutely necessary to go to the emergency room to solve the problem promptly. If not, the symptoms could cause serious complications, and even disability.
Why does Campylobacter infection develop?
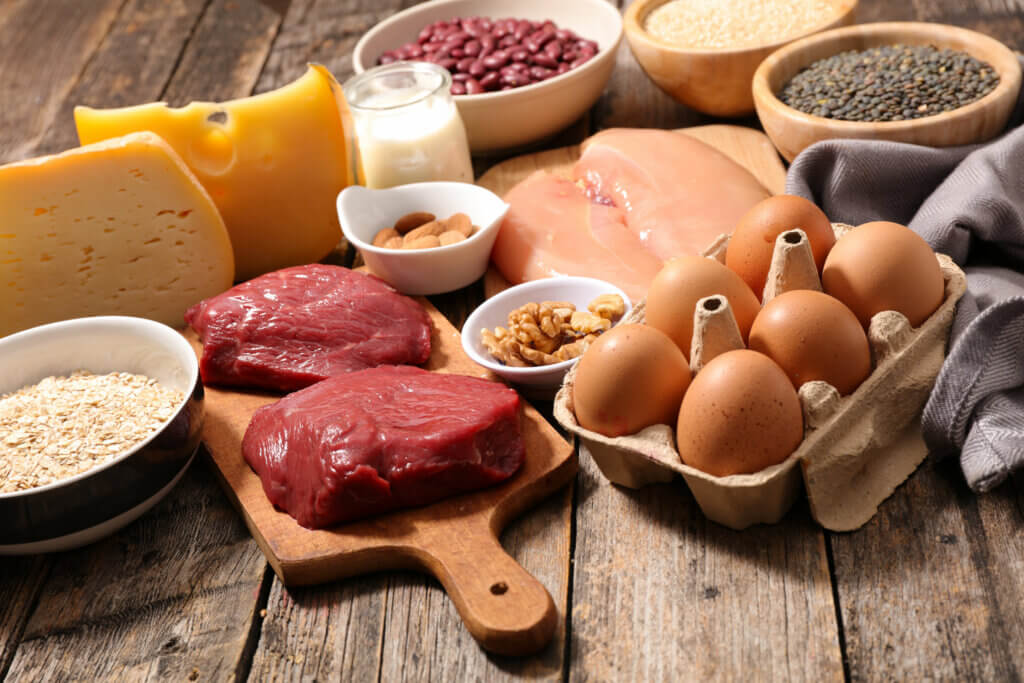

Bacteria of the genus Campylobacter are normally found in the digestive tract of many farm animals. Its presence is common, especially in birds and in animal feces. They can also get into the water, contaminating it.
Unpasteurized milk can also contain these microorganisms. To prevent this kind of problem, you need to ensure that you cook food correctly before consumption, as we’re talking about microorganisms that aren’t resistant to high temperatures.
However, many aspects are unknown in relation to the motility, survival, and virulence of this type of pathology. This is confirmed by research published in the journal Food Microbiology.
The number of bacteria ingested may be a determining factor in assessing the severity of the disease and the intensity of the symptoms, but the composition of the host’s microbiota may also play an important role.
We’re talking about a pathogen that spreads easily. Not only does it contaminate liquids, but it can also be passed from person to person through contact. For this reason, contagion is relatively frequent. To prevent this type of situation, precautions should be taken in terms of hygiene, among which we can highlight hand washing and cleaning surfaces correctly.
Although it’s true that animals are usually the reservoirs for this type of infection, it’s also possible to find plants that have been contaminated with the microorganism. It doesn’t occur very frequently, but it can happen.
Above all, this risk exists if the food has come into contact with fecal water or with the fecal mass of a carrier animal. To prevent this, chemical products are often used in crops at an industrial level.
How is Campylobacter diagnosed?
There are many infectious diseases with similar symptoms. It’s important to identify the causal agent in order to suggest an effective solution to the problem. A stool culture is usually required to diagnose Campylobacter infection. A blood sample may even be required for confirmation.
From this point on, treatment options can be assessed. However, there’s no specific option for the type of bacteria in question. Azithromycin is usually prescribed in the most complicated cases.
Even so, if the administration of this type of drug can be prevented, it’s better to opt for other alternatives. Continued use of them can lead to bacterial resistance, a problem that has proven to be increasingly common worldwide.
In addition, implementing a good hydration strategy to compensate for the loss of fluids from diarrhea will be crucial. If natural mineral water isn’t tolerated, an intravenous infusion should be used. The objective is to maintain the hydroelectrolytic balance and prevent cramps and alterations in the most basic and vital physiological processes.
One of the worst complications has to do with the passage of bacteria into the bloodstream. In this case, a more aggressive treatment with antibiotics such as imipenem or gentamicin should be started for 2 or 4 weeks. Otherwise, the patient’s life could be put at risk, from a process known as sepsis. This is confirmed by a study published in the Romanian Journal of Internal Medicine.
Prevention strategies
To prevent Campylobacter infection, you’ll need to implement a series of habits related to food hygiene. In the first place, you’ll have to ensure the proper cooking of foods of animal origin.
Meat from raw poultry should not be consumed, since the risk of contamination is high. You should ensure that the meat is exposed to a temperature of at least 65 degrees Centigrade (150 Fahrenheit) in order to kill bacteria.
Eggs can also be a vector for the transmission of the bacteria, as they can be in contact with the fecal mass of the birds. For this reason, great care must be taken with their consumption raw. When breaking them, contamination may be caused by the microorganisms present in the shell.
Likewise, if they’re kept at room temperature once opened, the risk of reproduction of the bacteria increases. In fact, in restaurants, their use is only allowed after a pasteurization process.
In the same way, good hand hygiene is essential, before and after handling raw food. Soap and water will suffice. This also avoids cross-contamination that can lead to infections of other foodstuffs.
Precautionary measures must be taken if someone who has been diagnosed with Campylobacter infection is living in your home. The bacteria are mainly transmitted through fecal matter, but hands could also be contaminated.
Neither must we forget the need to check the drinkability of the liquids we consume. This isn’t usually a problem in the case of bottled mineral water. However, when water is obtained from any source, it’s essential for it to pass certain quality controls periodically, in order to prevent infections.
Complications of Campylobacter infection
Campylobacter infection occurs with varying degrees of digestive symptoms, as we have described. However, it can get quite serious in some situations. This usually occurs especially in risk groups and in immunosuppressed people.
As the process worsens, arthritis could develop, although even this isn’t the worst case scenario. Sepsis is a truly worrying problem, and there are other associated syndromes.
One of them is the neurological disorder known as Guillain-Barré, as confirmed by research published in the Expert Review of Clinical Immunology. It can cause a polio-like paralysis that can lead to severe respiratory and neurological dysfunction. In the most extreme cases, it could end in death.
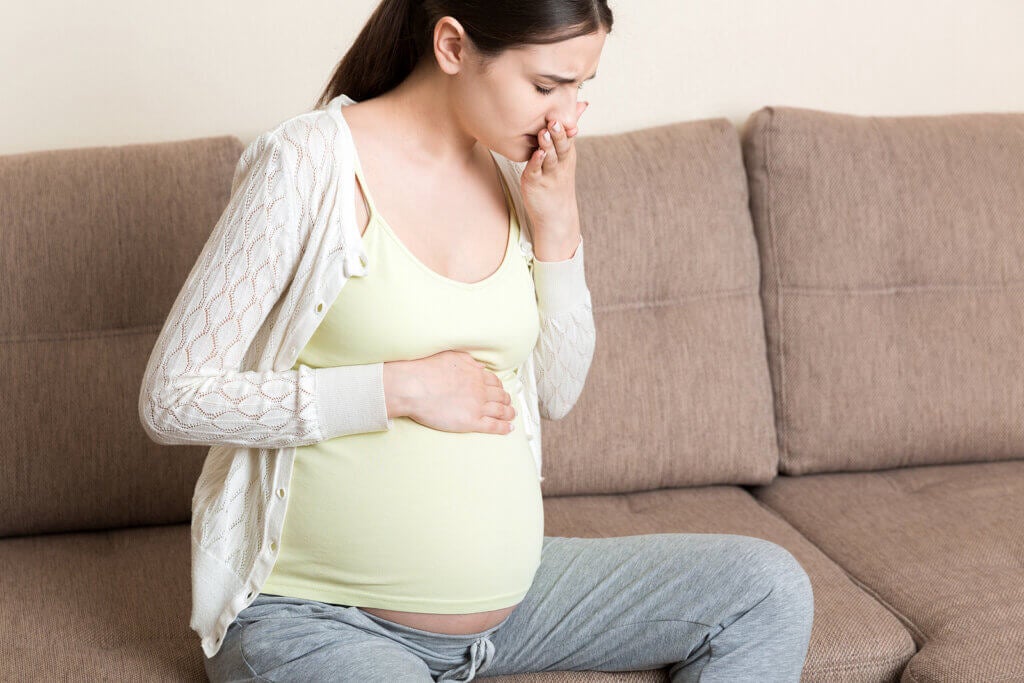
These types of bacterial infections are especially dangerous in the case of the elderly, and pregnant women.
The former have a greater risk of dehydration caused by vomiting and diarrhea. In the second case, the microorganisms could reach the fetus through the placenta, causing serious developmental damage. For this reason, it’s recommended to take extreme precautionary measures during this period, not consuming any type of raw food.
People who are under treatment with immunomodulatory agents are also at risk. In this case, the defense mechanisms of our bodies could be affected, meaning that they won’t be able to respond adequately to this type of infection. Normally it’s necessary to take extreme hygienic precautions if this class of drugs is consumed, in order to prevent complications.
Campylobacter infection, a serious food safety problem
Campylobacter infection occurs from consuming food or fluids contaminated with the bacteria. It’s a pathology that occurs with digestive symptoms of different intensities, and can become serious in specific situations. For this reason, it’s best to focus on prevention and to implement different food hygiene strategies.
When you think you may have any of the symptoms we’ve described, you should visit the doctor. They will be in charge of recommending treatment, if necessary. It’s very important to follow their instructions and, if they prescribe antibiotics, then you should finish the course. If you end the treatment halfway, it could cause bacterial resistance.
Campylobacter infection can be contracted from the consumption of contaminated food, and poultry meat is the most likely to contain this type of microorganism.
This pathology develops digestive-type symptoms and can also cause fever. However, some people can overcome it without any symptoms. Be that as it may, it’s still necessary to implement a series of food hygiene mechanisms to prevent potential risks.
Infectious pathologies caused by the consumption of food in poor condition or incorrectly handled are especially dangerous in the case of risk groups. Older people or pregnant women could experience many complications, as well are those who are immunosuppressed for different reasons. In these cases, it’s important to implement good prevention methods.
What are the symptoms of Campylobacter infection?
Normally, the typical symptoms of Campylobacter infection, according to a study published in the Clinics in Laboratory Medicine journal, are the following:
- Diarrhea, sometimes with blood
- Cramps
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
If these symptoms develop, it’s advisable to visit a doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and to implement a series of strategies to speed up healing. Sometimes the use of drugs will be necessary.
Other times it will be necessary to adjust the diet to prevent dehydration and malnutrition problems. In the most serious cases, antibiotics could even be administered to eliminate the infection.
It must be taken into account that, in the most severe cases of Campylobacter infection, reactive arthritis could develop. This is evidenced by research published in the journal Infectious Disease Clinics of North America.
In these cases, it would be absolutely necessary to go to the emergency room to solve the problem promptly. If not, the symptoms could cause serious complications, and even disability.
Why does Campylobacter infection develop?

Bacteria of the genus Campylobacter are normally found in the digestive tract of many farm animals. Its presence is common, especially in birds and in animal feces. They can also get into the water, contaminating it.
Unpasteurized milk can also contain these microorganisms. To prevent this kind of problem, you need to ensure that you cook food correctly before consumption, as we’re talking about microorganisms that aren’t resistant to high temperatures.
However, many aspects are unknown in relation to the motility, survival, and virulence of this type of pathology. This is confirmed by research published in the journal Food Microbiology.
The number of bacteria ingested may be a determining factor in assessing the severity of the disease and the intensity of the symptoms, but the composition of the host’s microbiota may also play an important role.
We’re talking about a pathogen that spreads easily. Not only does it contaminate liquids, but it can also be passed from person to person through contact. For this reason, contagion is relatively frequent. To prevent this type of situation, precautions should be taken in terms of hygiene, among which we can highlight hand washing and cleaning surfaces correctly.
Although it’s true that animals are usually the reservoirs for this type of infection, it’s also possible to find plants that have been contaminated with the microorganism. It doesn’t occur very frequently, but it can happen.
Above all, this risk exists if the food has come into contact with fecal water or with the fecal mass of a carrier animal. To prevent this, chemical products are often used in crops at an industrial level.
How is Campylobacter diagnosed?
There are many infectious diseases with similar symptoms. It’s important to identify the causal agent in order to suggest an effective solution to the problem. A stool culture is usually required to diagnose Campylobacter infection. A blood sample may even be required for confirmation.
From this point on, treatment options can be assessed. However, there’s no specific option for the type of bacteria in question. Azithromycin is usually prescribed in the most complicated cases.
Even so, if the administration of this type of drug can be prevented, it’s better to opt for other alternatives. Continued use of them can lead to bacterial resistance, a problem that has proven to be increasingly common worldwide.
In addition, implementing a good hydration strategy to compensate for the loss of fluids from diarrhea will be crucial. If natural mineral water isn’t tolerated, an intravenous infusion should be used. The objective is to maintain the hydroelectrolytic balance and prevent cramps and alterations in the most basic and vital physiological processes.
One of the worst complications has to do with the passage of bacteria into the bloodstream. In this case, a more aggressive treatment with antibiotics such as imipenem or gentamicin should be started for 2 or 4 weeks. Otherwise, the patient’s life could be put at risk, from a process known as sepsis. This is confirmed by a study published in the Romanian Journal of Internal Medicine.
Prevention strategies
To prevent Campylobacter infection, you’ll need to implement a series of habits related to food hygiene. In the first place, you’ll have to ensure the proper cooking of foods of animal origin.
Meat from raw poultry should not be consumed, since the risk of contamination is high. You should ensure that the meat is exposed to a temperature of at least 65 degrees Centigrade (150 Fahrenheit) in order to kill bacteria.
Eggs can also be a vector for the transmission of the bacteria, as they can be in contact with the fecal mass of the birds. For this reason, great care must be taken with their consumption raw. When breaking them, contamination may be caused by the microorganisms present in the shell.
Likewise, if they’re kept at room temperature once opened, the risk of reproduction of the bacteria increases. In fact, in restaurants, their use is only allowed after a pasteurization process.
In the same way, good hand hygiene is essential, before and after handling raw food. Soap and water will suffice. This also avoids cross-contamination that can lead to infections of other foodstuffs.
Precautionary measures must be taken if someone who has been diagnosed with Campylobacter infection is living in your home. The bacteria are mainly transmitted through fecal matter, but hands could also be contaminated.
Neither must we forget the need to check the drinkability of the liquids we consume. This isn’t usually a problem in the case of bottled mineral water. However, when water is obtained from any source, it’s essential for it to pass certain quality controls periodically, in order to prevent infections.
Complications of Campylobacter infection

Campylobacter infection occurs with varying degrees of digestive symptoms, as we have described. However, it can get quite serious in some situations. This usually occurs especially in risk groups and in immunosuppressed people.
As the process worsens, arthritis could develop, although even this isn’t the worst case scenario. Sepsis is a truly worrying problem, and there are other associated syndromes.
One of them is the neurological disorder known as Guillain-Barré, as confirmed by research published in the Expert Review of Clinical Immunology. It can cause a polio-like paralysis that can lead to severe respiratory and neurological dysfunction. In the most extreme cases, it could end in death.
These types of bacterial infections are especially dangerous in the case of the elderly, and pregnant women.
The former have a greater risk of dehydration caused by vomiting and diarrhea. In the second case, the microorganisms could reach the fetus through the placenta, causing serious developmental damage. For this reason, it’s recommended to take extreme precautionary measures during this period, not consuming any type of raw food.
People who are under treatment with immunomodulatory agents are also at risk. In this case, the defense mechanisms of our bodies could be affected, meaning that they won’t be able to respond adequately to this type of infection. Normally it’s necessary to take extreme hygienic precautions if this class of drugs is consumed, in order to prevent complications.
Campylobacter infection, a serious food safety problem
Campylobacter infection occurs from consuming food or fluids contaminated with the bacteria. It’s a pathology that occurs with digestive symptoms of different intensities, and can become serious in specific situations. For this reason, it’s best to focus on prevention and to implement different food hygiene strategies.
When you think you may have any of the symptoms we’ve described, you should visit the doctor. They will be in charge of recommending treatment, if necessary. It’s very important to follow their instructions and, if they prescribe antibiotics, then you should finish the course. If you end the treatment halfway, it could cause bacterial resistance.
- Schmitt S. K. (2017). Reactive Arthritis. Infectious disease clinics of North America, 31(2), 265–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2017.01.002.
- Fitzgerald C. (2015). Campylobacter. Clinics in laboratory medicine, 35(2), 289–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cll.2015.03.001.
- Bolton D. J. (2015). Campylobacter virulence and survival factors. Food microbiology, 48, 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2014.11.017.
- Purcarea, A., & Sovaila, S. (2020). Sepsis, a 2020 review for the internist. Romanian journal of internal medicine = Revue roumaine de medecine interne, 58(3), 129–137. https://doi.org/10.2478/rjim-2020-0012.
- Jasti, A. K., Selmi, C., Sarmiento-Monroy, J. C., Vega, D. A., Anaya, J. M., & Gershwin, M. E. (2016). Guillain-Barré syndrome: causes, immunopathogenic mechanisms and treatment. Expert review of clinical immunology, 12(11), 1175–1189. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2016.1193006.
- Wencewicz T. A. (2019). Crossroads of Antibiotic Resistance and Biosynthesis. Journal of molecular biology, 431(18), 3370–3399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2019.06.033.
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







