Varicose Veins: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention and Treatment
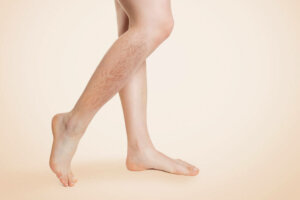
Venous circulation is a network of vessels of different types, in charge of returning blood from the organs to the heart. It has a valve system that allows it to do its job satisfactorily, however, valve failure can cause varicose veins.
The veins have a very thin muscular layer, and so they don’t maintain a constant pressure and, thus, make it difficult for venous return. This difficulty is greater in the lower limbs, which is why they have multiple mechanisms, from suction due to intra-abdominal pressure to venous valves.
These varicose veins can be defined in a simple way as the ‘pathological and permanent dilation of the veins, which usually has a tortuous arrangement’. They can appear in any area of the body, although they’re more frequent in the legs. Studies show that they affect up to 40% of the general population.
Symptoms
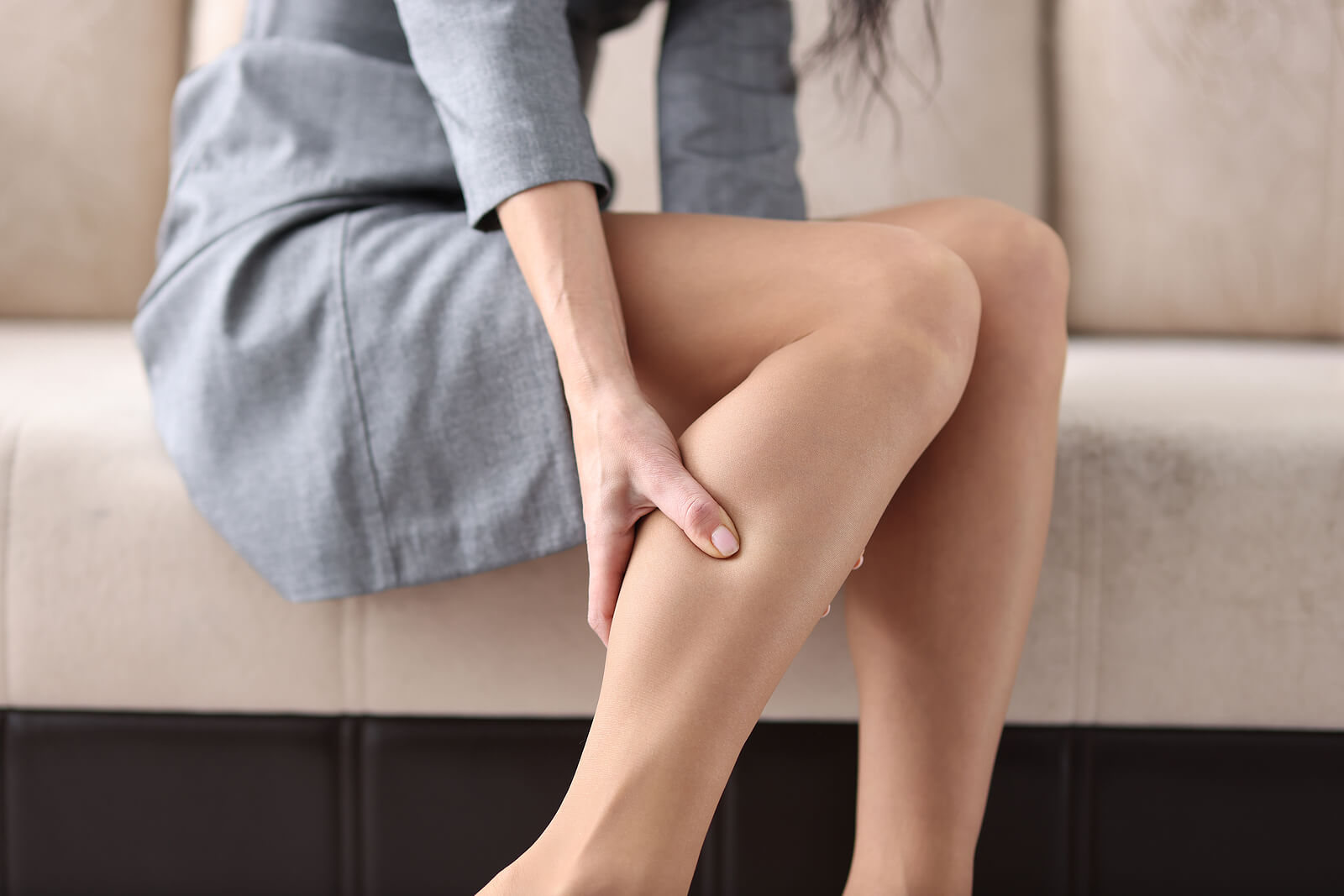

The lower limbs have both a superficial and a deep venous system, so varicose vein symptoms can vary depending on the affected system. In this sense, they’re not always visible when they’re in the deep veins, although they can be felt and be tense when the condition is developing.
However, they can gradually increase in size, stand out, and be much more obvious, especially when standing. In addition to the manifestation of veins on the skin, people may also report one or more of the following symptoms:
- A feeling of heaviness, fullness, and pain in the legs
- Edema similar to fluid retention
- Itching or stinging in the legs
- Frequent night cramps
- Smaller veins on the surface colored red or blue
If varicose veins are not treated in time, blood circulation in the lower limbs is more compromised, and a syndrome called deep vein insufficiency may appear. This is capable of generating various symptoms in the legs, among which the following stand out:
- Severe swelling
- Severe pain when sitting or standing for a long time
- Dry, flaky skin that breaks easily
- Changes in skin color
- The appearance of ulcers on the ankles that are difficult to heal
- The use of tight clothing and high-heeled shoes
Causes of varicose veins
In most cases, varicose veins have an unknown etiology, however, they are often associated with primary venous valve insufficiency.
This pathology is characterized by the incomplete closure of these valves, which generates the return of blood and the dilation of the veins.
Varicose veins can appear due to a weakness in the walls of the veins, primary or secondary to an injury. In this way, the vessels are unable to handle the large volumes of blood and tend to dilate.
Genetic factors have a certain influence on the appearance of the disease, according to various investigations.
It hasn’t yet been possible to link a specific gene with the alteration, however, most people who suffer from varicose veins have a family history of the disease.
Risk factor’s
Despite all the causes described, in many cases, it’s impossible to determine a specific cause. However, there are many situations that are capable of affecting the veins of the lower limbs.
In this way, it has been possible to identify a series of factors that predispose a person to the appearance of varicose veins, among which the following stand out:
- Being a woman
- Standing or sitting for a long time
- Obesity
- Variations in estrogen levels
- Advanced age
- Multiple pregnancies
Diagnosis
Fortunately, diagnosing varicose veins is very simple; the doctor will have to use both an interrogation and a physical examination. The specialist should first ask about the onset of symptoms and the circumstances of their appearance. Generally, pain and other symptoms appear after standing for long periods of time.
The physical examination is very useful in the diagnosis; through inspection, the doctor can confirm the presence of varicose veins. Also, they should look for some signs of chronic venous insufficiency such as ulcers or trophic changes in the skin. Tourniquet testing isn’t currently used.
Once the presence of varicose veins has been confirmed, the doctor should recommend an imaging test to assess the severity of the situation. The most frequently performed exam is an ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. However, x-rays and CT scans are also helpful.
Varicose vein treatment
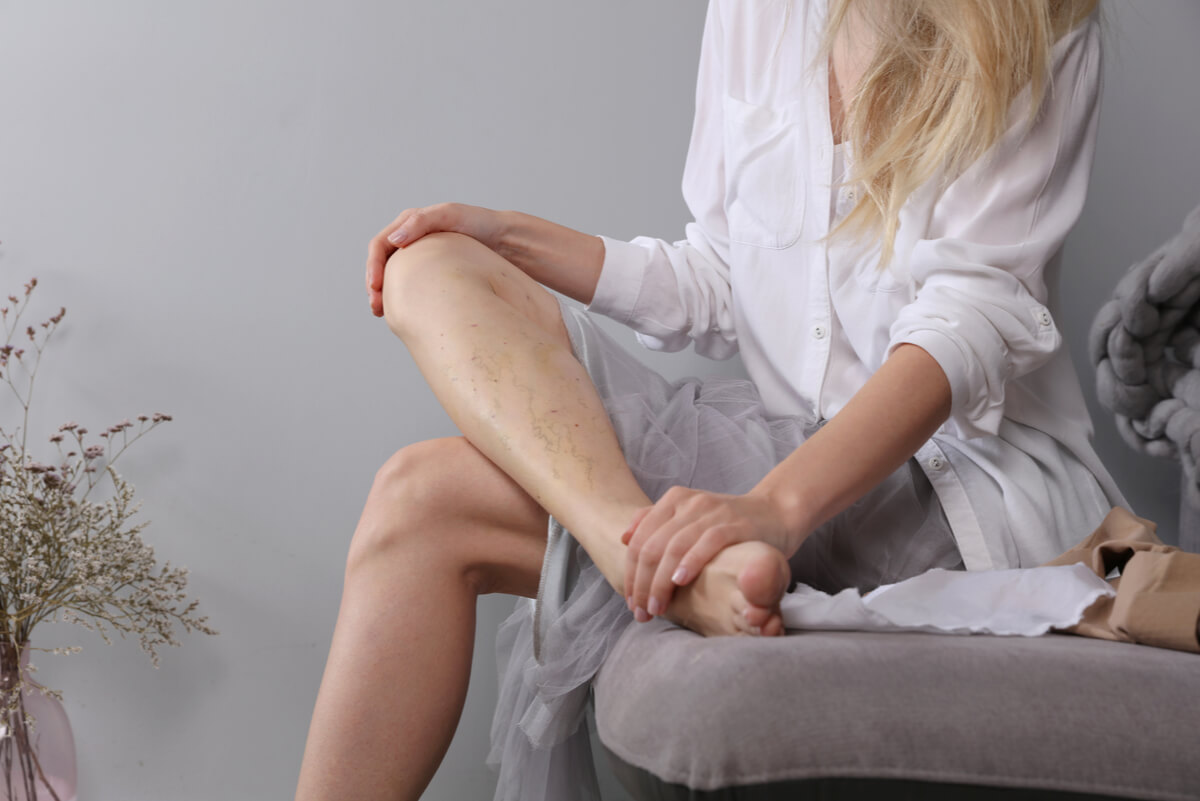

The treatment of this pathology will largely depend on the severity of the situation. In this sense, a minimally invasive treatment should be chosen in the mildest cases.
One of the indications will be to make changes in the diet and exercise frequently in order to reduce excess weight in addition to adequate hydration in case of skin changes.
Compression stockings are very useful for everyone who suffers from varicose veins. They slow down the progression of the pathology, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications, all of this is achieved by increasing the return of venous blood to the heart.
Certain drugs called phlebotonics are indicated to relieve edema and accelerate the healing of ulcers, although they disappear varicose veins or prevent their progression. On the other hand, there are more aggressive measures such as sclerotherapy and the extraction of the blood vessel, or phlebectomy.
Sclerotherapy is nothing more than the injection of an irritating substance inside the varicose vein that will cause it to heal and occlude. Phlebectomy is the surgical removal of the affected vein. Both procedures are very invasive, but it’s estimated that they have a success rate of up to 90%.
How to prevent the appearance of varicose veins?
Currently, there’s no 100% effective method that prevents the appearance of varicose veins since they are the product of the influence of many factors.
However, there are certain measures that can reduce the likelihood that the veins in the lower limbs will become dilated. Fortunately, such measurements are easy to perform.
The main method to prevent the appearance of varicose veins is to eliminate the risk factors mentioned above. In this sense, making a small change in lifestyle is usually very useful, so the following tips should be followed:
- Move your legs frequently
- Avoid standing or sitting for long periods
- Exercise consistently and eat a balanced diet
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Avoid obesity and being overweight
- Wear comfortable shoes
- Avoid tight clothing
A pathology that can get complicated
The appearance of varicose veins in the lower limbs is closely related to advanced age, which is why they can be looked down upon by many people. However, all patients with varicose dilation should seek medical attention to prevent the progression of the disease.
Varicose veins generate blood stasis in the lower limbs, which can favor the formation of thrombi. They can travel to any area of the body, obstruct a blood vessel, and cause severe damage. In this sense, it’s vitally important to seek specialized medical help and treat the pathology to avoid further damage.
Venous circulation is a network of vessels of different types, in charge of returning blood from the organs to the heart. It has a valve system that allows it to do its job satisfactorily, however, valve failure can cause varicose veins.
The veins have a very thin muscular layer, and so they don’t maintain a constant pressure and, thus, make it difficult for venous return. This difficulty is greater in the lower limbs, which is why they have multiple mechanisms, from suction due to intra-abdominal pressure to venous valves.
These varicose veins can be defined in a simple way as the ‘pathological and permanent dilation of the veins, which usually has a tortuous arrangement’. They can appear in any area of the body, although they’re more frequent in the legs. Studies show that they affect up to 40% of the general population.
Symptoms

The lower limbs have both a superficial and a deep venous system, so varicose vein symptoms can vary depending on the affected system. In this sense, they’re not always visible when they’re in the deep veins, although they can be felt and be tense when the condition is developing.
However, they can gradually increase in size, stand out, and be much more obvious, especially when standing. In addition to the manifestation of veins on the skin, people may also report one or more of the following symptoms:
- A feeling of heaviness, fullness, and pain in the legs
- Edema similar to fluid retention
- Itching or stinging in the legs
- Frequent night cramps
- Smaller veins on the surface colored red or blue
If varicose veins are not treated in time, blood circulation in the lower limbs is more compromised, and a syndrome called deep vein insufficiency may appear. This is capable of generating various symptoms in the legs, among which the following stand out:
- Severe swelling
- Severe pain when sitting or standing for a long time
- Dry, flaky skin that breaks easily
- Changes in skin color
- The appearance of ulcers on the ankles that are difficult to heal
- The use of tight clothing and high-heeled shoes
Causes of varicose veins
In most cases, varicose veins have an unknown etiology, however, they are often associated with primary venous valve insufficiency.
This pathology is characterized by the incomplete closure of these valves, which generates the return of blood and the dilation of the veins.
Varicose veins can appear due to a weakness in the walls of the veins, primary or secondary to an injury. In this way, the vessels are unable to handle the large volumes of blood and tend to dilate.
Genetic factors have a certain influence on the appearance of the disease, according to various investigations.
It hasn’t yet been possible to link a specific gene with the alteration, however, most people who suffer from varicose veins have a family history of the disease.
Risk factor’s
Despite all the causes described, in many cases, it’s impossible to determine a specific cause. However, there are many situations that are capable of affecting the veins of the lower limbs.
In this way, it has been possible to identify a series of factors that predispose a person to the appearance of varicose veins, among which the following stand out:
- Being a woman
- Standing or sitting for a long time
- Obesity
- Variations in estrogen levels
- Advanced age
- Multiple pregnancies
Diagnosis
Fortunately, diagnosing varicose veins is very simple; the doctor will have to use both an interrogation and a physical examination. The specialist should first ask about the onset of symptoms and the circumstances of their appearance. Generally, pain and other symptoms appear after standing for long periods of time.
The physical examination is very useful in the diagnosis; through inspection, the doctor can confirm the presence of varicose veins. Also, they should look for some signs of chronic venous insufficiency such as ulcers or trophic changes in the skin. Tourniquet testing isn’t currently used.
Once the presence of varicose veins has been confirmed, the doctor should recommend an imaging test to assess the severity of the situation. The most frequently performed exam is an ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. However, x-rays and CT scans are also helpful.
Varicose vein treatment

The treatment of this pathology will largely depend on the severity of the situation. In this sense, a minimally invasive treatment should be chosen in the mildest cases.
One of the indications will be to make changes in the diet and exercise frequently in order to reduce excess weight in addition to adequate hydration in case of skin changes.
Compression stockings are very useful for everyone who suffers from varicose veins. They slow down the progression of the pathology, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications, all of this is achieved by increasing the return of venous blood to the heart.
Certain drugs called phlebotonics are indicated to relieve edema and accelerate the healing of ulcers, although they disappear varicose veins or prevent their progression. On the other hand, there are more aggressive measures such as sclerotherapy and the extraction of the blood vessel, or phlebectomy.
Sclerotherapy is nothing more than the injection of an irritating substance inside the varicose vein that will cause it to heal and occlude. Phlebectomy is the surgical removal of the affected vein. Both procedures are very invasive, but it’s estimated that they have a success rate of up to 90%.
How to prevent the appearance of varicose veins?
Currently, there’s no 100% effective method that prevents the appearance of varicose veins since they are the product of the influence of many factors.
However, there are certain measures that can reduce the likelihood that the veins in the lower limbs will become dilated. Fortunately, such measurements are easy to perform.
The main method to prevent the appearance of varicose veins is to eliminate the risk factors mentioned above. In this sense, making a small change in lifestyle is usually very useful, so the following tips should be followed:
- Move your legs frequently
- Avoid standing or sitting for long periods
- Exercise consistently and eat a balanced diet
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Avoid obesity and being overweight
- Wear comfortable shoes
- Avoid tight clothing
A pathology that can get complicated
The appearance of varicose veins in the lower limbs is closely related to advanced age, which is why they can be looked down upon by many people. However, all patients with varicose dilation should seek medical attention to prevent the progression of the disease.
Varicose veins generate blood stasis in the lower limbs, which can favor the formation of thrombi. They can travel to any area of the body, obstruct a blood vessel, and cause severe damage. In this sense, it’s vitally important to seek specialized medical help and treat the pathology to avoid further damage.
- Tabares E, Sánchez-Coll S. Enfermedad vascular periférica: problemas venosos de miembros inferiores. Estudio de la Incapacidad Laboral por Enfermedades Cardiocirculatórias, Madrid. Instituto Nacional de Medicina y Seguridad del Trabajo. (1998): 173-82.
- Azcona L. Insuficiencia venosa. Prevención y tratamiento. Farmacia Profesional. 2008; 22(10): 36-44.
- Ducajú Moñux G. Enfermedades de las venas. Varices y trombosis venosa profunda. Libro de la salud cardiovascular del Hospital Clínico San Carlos y la Fundación BBVA. 2009: 537-48.
- Rabe E, Pannier F. Embolization is not essential in the treatment of leg varices due to pelvic venous insufficiency. Phlebology. 2015;30(1 Suppl):86-8.
- Greiner M, Gilling-Smith GL. Leg varices originating from the pelvis: diagnosis and treatment. Vascular. 2007;15(2):70-8.
- Rezaie ES, Maas M, van der Horst CMAM. Episodes of extreme lower leg pain caused by intraosseous varicose veins. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018:bcr2017223986.
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







