Everything You Need to Know About Breast Cancer

Oncological diseases are among the most feared group of pathologies. One of the most common malignancies in women is breast cancer. It appears due to the abnormal and uncontrolled proliferation of the cells of the mammary gland, which can be life-threatening. Find out all you need to know about breast cancer here.
The incidence of this disease has increased in recent years. In fact, studies claim that it accounts for up to 25% of all cancers in women. It can affect people of any age, even men.
Today, there are many diagnostic tests that allow early identification of cancer. Diagnosis in the early stages improves the prognosis considerably.
Symptoms of breast cancer
One of the most common symptoms of the disease is the presence of a lump in the affected breast or in the axillary region. The tumor is usually solid, painless, and immobile, with irregular borders and a variable size, depending on the stage it’s found in.
In some cases, it can cause changes in the affected breast that are more obvious than the lump itself. In this sense, women should be attentive to the following manifestations:
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast
- The appearance of small dimples in the skin of the breast, similar to the peel of the orange
- Retraction or inversion of the nipple
- Expulsion of abnormal secretions through the nipple
- Redness and peeling of the areola-nipple complex
- Ulceration of the breast
All these manifestations can appear in the most advanced stages of the disease and in the most aggressive types of cancer. It’s vitally important to seek medical assistance in the presence of any of the symptoms described.
Types of breast cancer
The mammary gland has different lobules where breast milk is produced and with ducts responsible for transporting it to the nipple. In general terms, breast cancer can be divided into 2 groups, according to the part of the gland that’s affected. The main forms of presentation are ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma.
Ductal carcinoma is one that’s found in the milk ducts, that is, in those responsible for transporting breast milk. On the other hand, lobular carcinoma appears when the cells of the breast lobules are affected. Both carcinomas can be divided into in situ and invasive.
Multiple studies show that invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type, accounting for between 60% and 80% of all cases. It can be aggressive and fast-growing.
Among the less frequent forms of presentation of breast cancer, the following stand out:
- Triple-negative breast cancer
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Paget’s disease
- Angiosarcoma
- Phyllodes tumor
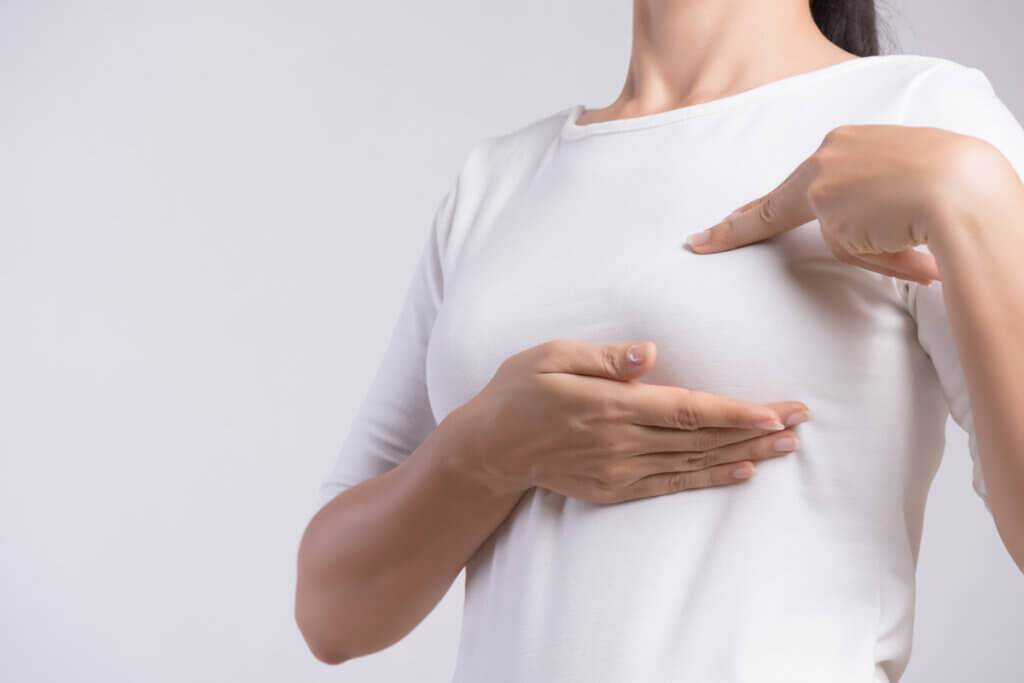

Causes and risk factors
Unfortunately, the causes of breast cancer haven’t yet been determined. It’s believed that the action of estrogens on breast tissue may favor the appearance of the tumor.
It’s known that breast cancer is linked to a series of risk factors. Many of these are related to an unhealthy lifestyle, so they can be modified.
Other factors are unchangeable. One of the most important is the mutation in the BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 genes. Studies show that these mutations are found in up to 10% of all cancer cases detected worldwide.
On the other hand, other risk factors that must be taken into account are the following:
- Being a woman and be over 45 years old
- Being obese or overweight
- Early menarche or late menopause
- Receive hormone replacement therapy during menopause
- Consuming alcoholic beverages
- Not having had children nor having breastfed
- Having a personal or family history of breast cancer
Diagnosis of breast cancer
The doctor should question the patient and carry out a complete physical examination in order to determine the signs and symptoms of the disease. The specialist should also look at the affected breast and palpate it to look for an abnormal lump.
In spite of everything, the definitive diagnosis of breast cancer is obtained after performing an imaging test and a biopsy. The most widely used image for detecting the disease is mammography. It uses low-dose X-rays to obtain an image of the breast tissue and study the tumor.
Other imaging tests that may be helpful are breast ultrasound and computed tomography. Once the presence of a tumor with signs of malignancy is determined, the specialist will indicate a biopsy. This procedure consists of removing the lesion or a sample of it in order to study it under the microscope.
Biopsies provide more detailed information about the disease and its stage. Carrying out this step is essential to decide the therapy.
Treatment
The main therapeutic option to fight breast cancer is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the mammary gland. The procedure in question is known as a mastectomy and can be radical or partial. In radical mastectomy, the entire gland will be removed, while in partial mastectomy, only the affected tissue and a surrounding portion are removed.
Some types of breast cancer can spread through the lymph nodes, so the sentinel node study is done during the operation. The lymph node where the affected area drains is analyzed for metastases. This study is very reliable and research shows that it is 98% accurate.
On the other hand, the use of chemotherapy and radiotherapy can also be useful in the treatment of the condition. Both procedures reduce the size of the tumor before performing a mastectomy. In addition, they serve in the most advanced stages.
There are other therapeutic techniques for breast cancer, including targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy. However, their application will depend on the particular characteristics of the tumor.
Prevention of breast cancer
Unfortunately, there’s no 100% effective method to prevent breast cancer. However, its probability of occurrence can be reduced. It’s important to remember that the disease is associated with multiple risk factors, dependent on lifestyle.
It’s recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, with a balanced diet and also to perform some type of physical activity. It’s also possible to follow the following recommendations:
- Losing weight
- Reducing the consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Giving up smoking
- Not receiving hormone replacement therapy after menopause
And, even though it isn’t a recommendation as such, it’s also clear that having children and breastfeeding is a preventive factor.
On the other hand, it’s also recommended that women perform a breast self-examination every month. This will make it possible to detect any abnormal tumors early. It should be done between 5 and 7 days after menstruation.
A disease that usually has a good prognosis
Breast cancer is an oncological pathology suffered by millions of people around the world. It has a good prognosis when diagnosed in its early stages. Most people can be completely cured if the tumor is small.
On the other hand, diagnosis in advanced stages is associated with a low life expectancy, especially if there is metastasis to distant organs. In this sense, it’s essential to consult the doctor immediately in the presence of any abnormality in the breasts.
Oncological diseases are among the most feared group of pathologies. One of the most common malignancies in women is breast cancer. It appears due to the abnormal and uncontrolled proliferation of the cells of the mammary gland, which can be life-threatening. Find out all you need to know about breast cancer here.
The incidence of this disease has increased in recent years. In fact, studies claim that it accounts for up to 25% of all cancers in women. It can affect people of any age, even men.
Today, there are many diagnostic tests that allow early identification of cancer. Diagnosis in the early stages improves the prognosis considerably.
Symptoms of breast cancer
One of the most common symptoms of the disease is the presence of a lump in the affected breast or in the axillary region. The tumor is usually solid, painless, and immobile, with irregular borders and a variable size, depending on the stage it’s found in.
In some cases, it can cause changes in the affected breast that are more obvious than the lump itself. In this sense, women should be attentive to the following manifestations:
- Changes in the size or shape of the breast
- The appearance of small dimples in the skin of the breast, similar to the peel of the orange
- Retraction or inversion of the nipple
- Expulsion of abnormal secretions through the nipple
- Redness and peeling of the areola-nipple complex
- Ulceration of the breast
All these manifestations can appear in the most advanced stages of the disease and in the most aggressive types of cancer. It’s vitally important to seek medical assistance in the presence of any of the symptoms described.
Types of breast cancer
The mammary gland has different lobules where breast milk is produced and with ducts responsible for transporting it to the nipple. In general terms, breast cancer can be divided into 2 groups, according to the part of the gland that’s affected. The main forms of presentation are ductal carcinoma and lobular carcinoma.
Ductal carcinoma is one that’s found in the milk ducts, that is, in those responsible for transporting breast milk. On the other hand, lobular carcinoma appears when the cells of the breast lobules are affected. Both carcinomas can be divided into in situ and invasive.
Multiple studies show that invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type, accounting for between 60% and 80% of all cases. It can be aggressive and fast-growing.
Among the less frequent forms of presentation of breast cancer, the following stand out:
- Triple-negative breast cancer
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Paget’s disease
- Angiosarcoma
- Phyllodes tumor

Causes and risk factors
Unfortunately, the causes of breast cancer haven’t yet been determined. It’s believed that the action of estrogens on breast tissue may favor the appearance of the tumor.
It’s known that breast cancer is linked to a series of risk factors. Many of these are related to an unhealthy lifestyle, so they can be modified.
Other factors are unchangeable. One of the most important is the mutation in the BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 genes. Studies show that these mutations are found in up to 10% of all cancer cases detected worldwide.
On the other hand, other risk factors that must be taken into account are the following:
- Being a woman and be over 45 years old
- Being obese or overweight
- Early menarche or late menopause
- Receive hormone replacement therapy during menopause
- Consuming alcoholic beverages
- Not having had children nor having breastfed
- Having a personal or family history of breast cancer
Diagnosis of breast cancer
The doctor should question the patient and carry out a complete physical examination in order to determine the signs and symptoms of the disease. The specialist should also look at the affected breast and palpate it to look for an abnormal lump.
In spite of everything, the definitive diagnosis of breast cancer is obtained after performing an imaging test and a biopsy. The most widely used image for detecting the disease is mammography. It uses low-dose X-rays to obtain an image of the breast tissue and study the tumor.
Other imaging tests that may be helpful are breast ultrasound and computed tomography. Once the presence of a tumor with signs of malignancy is determined, the specialist will indicate a biopsy. This procedure consists of removing the lesion or a sample of it in order to study it under the microscope.
Biopsies provide more detailed information about the disease and its stage. Carrying out this step is essential to decide the therapy.
Treatment
The main therapeutic option to fight breast cancer is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the mammary gland. The procedure in question is known as a mastectomy and can be radical or partial. In radical mastectomy, the entire gland will be removed, while in partial mastectomy, only the affected tissue and a surrounding portion are removed.
Some types of breast cancer can spread through the lymph nodes, so the sentinel node study is done during the operation. The lymph node where the affected area drains is analyzed for metastases. This study is very reliable and research shows that it is 98% accurate.
On the other hand, the use of chemotherapy and radiotherapy can also be useful in the treatment of the condition. Both procedures reduce the size of the tumor before performing a mastectomy. In addition, they serve in the most advanced stages.
There are other therapeutic techniques for breast cancer, including targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy. However, their application will depend on the particular characteristics of the tumor.

Prevention of breast cancer
Unfortunately, there’s no 100% effective method to prevent breast cancer. However, its probability of occurrence can be reduced. It’s important to remember that the disease is associated with multiple risk factors, dependent on lifestyle.
It’s recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, with a balanced diet and also to perform some type of physical activity. It’s also possible to follow the following recommendations:
- Losing weight
- Reducing the consumption of alcoholic beverages
- Giving up smoking
- Not receiving hormone replacement therapy after menopause
And, even though it isn’t a recommendation as such, it’s also clear that having children and breastfeeding is a preventive factor.
On the other hand, it’s also recommended that women perform a breast self-examination every month. This will make it possible to detect any abnormal tumors early. It should be done between 5 and 7 days after menstruation.
A disease that usually has a good prognosis
Breast cancer is an oncological pathology suffered by millions of people around the world. It has a good prognosis when diagnosed in its early stages. Most people can be completely cured if the tumor is small.
On the other hand, diagnosis in advanced stages is associated with a low life expectancy, especially if there is metastasis to distant organs. In this sense, it’s essential to consult the doctor immediately in the presence of any abnormality in the breasts.
- Soto Flores W. Cáncer de mama. Revista Médica de Costa Rica y Centroamérica. 2015; 71(617): 799-802.
- Weigelt B, Geyer FC, Reis-Filho JS. Histological types of breast cancer: how special are they? Mol Oncol. 2010;4(3):192-208.
- Sun YS, Zhao Z, Yang ZN, Xu F et al. Risk Factors and Preventions of Breast Cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(11):1387-1397.
- McDonald ES, Clark AS, Tchou J, Zhang P et al. Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Breast Cancer. J Nucl Med. 2016;57 Suppl 1:9S-16S.
- Coughlin SS. Epidemiology of Breast Cancer in Women. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1152:9-29.
- Thorat MA, Balasubramanian R. Breast cancer prevention in high-risk women. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;65:18-31.
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







