What Is a Boil and How to Treat It?
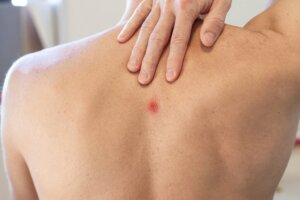
When the skin becomes infected, it can produce various lesions. Some of the best known (and common) are blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, nodules and ingrown hair cysts, for example. But what is a boil? Can we include it in this list or not?
A boil is a lump that occurs as a result of an infection of a hair follicle in the skin. It is tender to the touch, and as it fills with pus, the swelling and discomfort increase.
Sometimes boils are mistaken for spider bites or even acne pimples. However, they are not. Below we’ll tell you more about its causes, symptoms and other characteristics, as well as forms of treatment and prevention.
Symptoms

A boil is a lesion that usually appears frequently in areas such as the face, neck and hairy areas where there’s more friction and sweating, such as the armpits, thighs, groin and buttocks.
The bump is reddish in color. As it fills more and more with pus, it increases in size (it can even reach 5 centimeters – 2 inches). Thus, it becomes increasingly sensitive to touch.
In some cases, it can cause pain both at the point where it’s located and in the surrounding skin. The skin around the bump may also become swollen and red.
As it progresses, a light yellowish (or yellowish-white) tip forms on the boil, which usually then breaks open and allows the pus to drain. When this happens spontaneously, the sensitivity or pain improves.
- When drainage doesn’t occur spontaneously, it can be drained manually, but preferably by a doctor to prevent the infection from worsening.
- When several boils join, they form a more extensive lesion and are called anthrax, anthrax, or furunculosis.
- In the case of anthrax, the person may experience fever, fatigue, and general malaise, among others.
Causes
Boils sometimes appear on the skin where there has been a small injury or insect bite, because these are an easy entry point for bacteria. However, as Mayo Clinic experts explain, the cause of the boil is the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
Risk factor’s
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Poor hygiene
- Immunodeficiency
- Skin disorders (acne, eczema, etc.)
- Close contact with a person infected with staph
Treatment

The boil can disappear in a couple of weeks, approximately, without treatment as such but some basic self-care:
- Apply warm, moist compresses to the boil several times a day to soften it and promote spontaneous drainage.
- Never attempt to pierce with a home instrument or squeeze a boil with your hands, as it can make the boil worse and spread the infection.
- It’s important to apply a clean, moist and warm cotton or gauze several times a day. Cloths should never be reused.
- Only if the doctor authorizes it, should you resort to the use of an antibiotic.
If, after 2 weeks, the boil does not heal, and there’s fever and other symptoms, it will be necessary to see a doctor for proper treatment. It is also necessary to do it when the boil is located in the middle of the face or spine.
It isn’t recommended to manipulate, rub in any way (and certainly not vigorously) these types of lesions to try to drain them and make them disappear more quickly. This could be counterproductive, as well as painful and uncomfortable.
It is necessary to always bear in mind that, if you have any concerns or doubts about what to do in case of having an injury such as a boil, it is always best to consult a doctor.
Complications
- The complications that a boil can cause are not common. Bacteria from the boil rarely get into the bloodstream and spread to other parts of the body (causing septicemia).
- Septicemia can lead to infections of the heart (endocarditis) and bones (osteomyelitis).
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of staph infections and boils, it is necessary to maintain good hygiene habits in general, although regular hand washing stands out as the main prevention gesture. Notably, this is helpful in preventing boils and many other health problems.
At the same time, it will be essential to avoid sharing objects for personal use. This ranges from towels, sheets, and razors to sports equipment.
Another preventive measure is to keep wounds covered to prevent infection and to clean them properly while they heal.
Finally, it is important to point out that both when it comes to preventing and treating a boil, it is essential to wash and dry well everything that may be in contact with it: clothes, sheets, towels, etc.
When the skin becomes infected, it can produce various lesions. Some of the best known (and common) are blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, nodules and ingrown hair cysts, for example. But what is a boil? Can we include it in this list or not?
A boil is a lump that occurs as a result of an infection of a hair follicle in the skin. It is tender to the touch, and as it fills with pus, the swelling and discomfort increase.
Sometimes boils are mistaken for spider bites or even acne pimples. However, they are not. Below we’ll tell you more about its causes, symptoms and other characteristics, as well as forms of treatment and prevention.
Symptoms

A boil is a lesion that usually appears frequently in areas such as the face, neck and hairy areas where there’s more friction and sweating, such as the armpits, thighs, groin and buttocks.
The bump is reddish in color. As it fills more and more with pus, it increases in size (it can even reach 5 centimeters – 2 inches). Thus, it becomes increasingly sensitive to touch.
In some cases, it can cause pain both at the point where it’s located and in the surrounding skin. The skin around the bump may also become swollen and red.
As it progresses, a light yellowish (or yellowish-white) tip forms on the boil, which usually then breaks open and allows the pus to drain. When this happens spontaneously, the sensitivity or pain improves.
- When drainage doesn’t occur spontaneously, it can be drained manually, but preferably by a doctor to prevent the infection from worsening.
- When several boils join, they form a more extensive lesion and are called anthrax, anthrax, or furunculosis.
- In the case of anthrax, the person may experience fever, fatigue, and general malaise, among others.
Causes
Boils sometimes appear on the skin where there has been a small injury or insect bite, because these are an easy entry point for bacteria. However, as Mayo Clinic experts explain, the cause of the boil is the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
Risk factor’s
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Poor hygiene
- Immunodeficiency
- Skin disorders (acne, eczema, etc.)
- Close contact with a person infected with staph
Treatment

The boil can disappear in a couple of weeks, approximately, without treatment as such but some basic self-care:
- Apply warm, moist compresses to the boil several times a day to soften it and promote spontaneous drainage.
- Never attempt to pierce with a home instrument or squeeze a boil with your hands, as it can make the boil worse and spread the infection.
- It’s important to apply a clean, moist and warm cotton or gauze several times a day. Cloths should never be reused.
- Only if the doctor authorizes it, should you resort to the use of an antibiotic.
If, after 2 weeks, the boil does not heal, and there’s fever and other symptoms, it will be necessary to see a doctor for proper treatment. It is also necessary to do it when the boil is located in the middle of the face or spine.
It isn’t recommended to manipulate, rub in any way (and certainly not vigorously) these types of lesions to try to drain them and make them disappear more quickly. This could be counterproductive, as well as painful and uncomfortable.
It is necessary to always bear in mind that, if you have any concerns or doubts about what to do in case of having an injury such as a boil, it is always best to consult a doctor.
Complications
- The complications that a boil can cause are not common. Bacteria from the boil rarely get into the bloodstream and spread to other parts of the body (causing septicemia).
- Septicemia can lead to infections of the heart (endocarditis) and bones (osteomyelitis).
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of staph infections and boils, it is necessary to maintain good hygiene habits in general, although regular hand washing stands out as the main prevention gesture. Notably, this is helpful in preventing boils and many other health problems.
At the same time, it will be essential to avoid sharing objects for personal use. This ranges from towels, sheets, and razors to sports equipment.
Another preventive measure is to keep wounds covered to prevent infection and to clean them properly while they heal.
Finally, it is important to point out that both when it comes to preventing and treating a boil, it is essential to wash and dry well everything that may be in contact with it: clothes, sheets, towels, etc.
- Ántrax: MedlinePlus enciclopedia médica [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 10]. Available from: https://medlineplus.gov/spanish/ency/article/000825.htm
- Dhar DA. Foliculitis y abscesos cutáneos – Trastornos de la piel [Internet]. Manual MSD versión para público general. 2019 [cited 2021 Jul 9]. Available from: https://www.msdmanuals.com/es/hogar/trastornos-de-la-piel/infecciones-bacterianas-de-la-piel/foliculitis-y-abscesos-cutáneos
- Forúnculos y ántrax – Diagnóstico y tratamiento – Mayo Clinic [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 10]. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/es-es/diseases-conditions/boils-and-carbuncles/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353776
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







