Symptoms of Anaphylaxis
Learning to identify the symptoms of anaphylaxis and learning more about it in general is an important preventive measure for everyone. This is largely because, if anaphylaxis isn’t identified and treated in time, it can become life-threatening.
And, just like a hypertensive emergency, overdoses, poisonings, seizures, signs of a heart attack or a heart attack itself, it’s considered to be a medical emergency.
By anaphylaxis, we mean a series of extremely serious and dangerous allergic reactions that a person can experience. It occurs abruptly and progresses rapidly, causing various symptoms including skin reactions and respiratory collapse.
We’ll now look at each of these symptoms in order to take the best precautions and, if necessary, to know when to ask for help and what to do while it arrives.
Common symptoms of anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a very dangerous acute hypersensitivity reaction, given its rapid evolution and its multisystemic and generalized impact. As the MSD Manual points out: “Anaphylactic reactions usually begin quickly, within a maximum period of 15 minutes after being close to the offending allergen.”
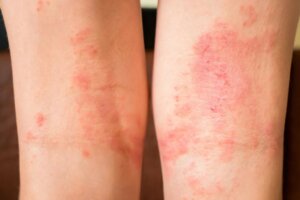
Skin reactions

Apart from noticing an intense itching sensation all over the body (pruritus), the person may develop hives. This is manifested through red bumps (which, when pressed, turn white). Also, bloating is another of the most common symptoms of anaphylaxis.
- The eyes, lips, tongue, and throat swell rapidly
- The redness of the eyes occurs suddenly, as in cases of irritation
Trouble breathing
Shortness of breath is seen in more than 70% of anaphylaxis cases. They’re usually related to a swelling of the face and throat, tightness in the chest, and wheezing, which are also part of the symptoms of anaphylaxis. They usually occur almost simultaneously, along with others.
Digestive symptoms
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and even colic are symptoms that could occur with anaphylaxis. This shows us the extent of these types of reactions and, once again, they make us realize the danger they pose.
Hypotension and other symptoms

All of the aforementioned symptoms of anaphylaxis may be accompanied by great anxiety, as well as confusion, speech difficulties, and extreme fear of the sensation of impending death.
On the other hand, in the upper respiratory system, you may experience congestion, a runny nose and sneezing. And, in addition to the aforementioned swelling in the face and throat, the person may notice an intense feeling of choking or hoarseness.
Along with the above, the heart may beat slower or faster than normal. Low blood pressure often occurs, and consequently, the person experiences weakness, dizziness and may even pass out.
When you observe confusion, weakness, dizziness, and great difficulties in breathing and speaking, followed by the person falling unconscious, anaphylactic shock is declared.
Rare or late symptoms
According to Dr. Peter J. Delves, in some cases, reactions can occur 4 to 8 hours after being exposed to the allergen. Symptoms can be limited to hives or include several of the above, and they can even be more deadly.
When to go to the doctor?
As we’ve seen, when it comes to comprehensive health and wellness, the best medicine can be prevented in many cases. Because of this, health experts never stop emphasizing how important it is to take care of yourself every day.
In the case of anaphylaxis, you should take into account everything we’ve mentioned in this article, and, if you have any questions regarding daily self-care, see a doctor.
Last but not least, if you identify the aforementioned symptoms of anaphylaxis, call the emergency department immediately so that they can administer the most appropriate treatment.
Learning to identify the symptoms of anaphylaxis and learning more about it in general is an important preventive measure for everyone. This is largely because, if anaphylaxis isn’t identified and treated in time, it can become life-threatening.
And, just like a hypertensive emergency, overdoses, poisonings, seizures, signs of a heart attack or a heart attack itself, it’s considered to be a medical emergency.
By anaphylaxis, we mean a series of extremely serious and dangerous allergic reactions that a person can experience. It occurs abruptly and progresses rapidly, causing various symptoms including skin reactions and respiratory collapse.
We’ll now look at each of these symptoms in order to take the best precautions and, if necessary, to know when to ask for help and what to do while it arrives.
Common symptoms of anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a very dangerous acute hypersensitivity reaction, given its rapid evolution and its multisystemic and generalized impact. As the MSD Manual points out: “Anaphylactic reactions usually begin quickly, within a maximum period of 15 minutes after being close to the offending allergen.”
Skin reactions

Apart from noticing an intense itching sensation all over the body (pruritus), the person may develop hives. This is manifested through red bumps (which, when pressed, turn white). Also, bloating is another of the most common symptoms of anaphylaxis.
- The eyes, lips, tongue, and throat swell rapidly
- The redness of the eyes occurs suddenly, as in cases of irritation
Trouble breathing
Shortness of breath is seen in more than 70% of anaphylaxis cases. They’re usually related to a swelling of the face and throat, tightness in the chest, and wheezing, which are also part of the symptoms of anaphylaxis. They usually occur almost simultaneously, along with others.
Digestive symptoms
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and even colic are symptoms that could occur with anaphylaxis. This shows us the extent of these types of reactions and, once again, they make us realize the danger they pose.
Hypotension and other symptoms

All of the aforementioned symptoms of anaphylaxis may be accompanied by great anxiety, as well as confusion, speech difficulties, and extreme fear of the sensation of impending death.
On the other hand, in the upper respiratory system, you may experience congestion, a runny nose and sneezing. And, in addition to the aforementioned swelling in the face and throat, the person may notice an intense feeling of choking or hoarseness.
Along with the above, the heart may beat slower or faster than normal. Low blood pressure often occurs, and consequently, the person experiences weakness, dizziness and may even pass out.
When you observe confusion, weakness, dizziness, and great difficulties in breathing and speaking, followed by the person falling unconscious, anaphylactic shock is declared.
Rare or late symptoms
According to Dr. Peter J. Delves, in some cases, reactions can occur 4 to 8 hours after being exposed to the allergen. Symptoms can be limited to hives or include several of the above, and they can even be more deadly.
When to go to the doctor?
As we’ve seen, when it comes to comprehensive health and wellness, the best medicine can be prevented in many cases. Because of this, health experts never stop emphasizing how important it is to take care of yourself every day.
In the case of anaphylaxis, you should take into account everything we’ve mentioned in this article, and, if you have any questions regarding daily self-care, see a doctor.
Last but not least, if you identify the aforementioned symptoms of anaphylaxis, call the emergency department immediately so that they can administer the most appropriate treatment.
-
“Datos Clave: Reacciones Anafilácticas .” n.d. Manual Merck Versión Para El Público General. Accessed June 15, 2021. https://www.merckmanuals.com/es-pr/hogar/breve-información-trastornos-inmunológicos/reacciones-alérgicas-y-otros-trastornos-de-hipersensibilidad/reacciones-anafilácticas.
-
Delves, Peter J. 2020. “Anafilaxia – Inmunología y Trastornos Alérgicos.” In Manual MSD Versión Para Profesionales. https://www.msdmanuals.com/es/professional/inmunología-y-trastornos-alérgicos/enfermedades-alérgicas,-autoinmunitarias-y-otros-trastornos-por-hipersensibilidad/anafilaxia.
-
Gómez Ayala, Adela-Emilia. 2011. “Anafilaxia. Clínica y Tratamiento.” Offarm 30 (2): 70–78. https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-offarm-4-articulo-anafilaxia-clinica-tratamiento-X0212047X11011351.
- McLendon K, Sternard BT. Anaphylaxis. [Updated 2020 Jun 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482124/
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







