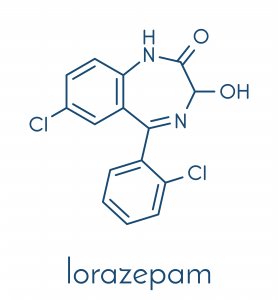
What Is Lorazepam?

Lorazepam is also known by its trade name Orfidal. It’s a drug that’s considered to be psychotropic because it acts on the Central Nervous System (CNS). Their action can affect the consumer’s mood and behavior. At present, it’s one of the most consumed drugs in Europe.
What is lorazepam used for?
Lorazepam is a drug used primarily to reduce pathological anxiety. It can also be used in some cases for sleep disorders, such as insomnia, and for nervous and emotional disorders.
Anxiety is a vital defense mechanism of the body, which is triggered in the face of a threat, and which allows us to face it. But if this anxiety isn’t proportionate to the triggering threat, in duration or intensity, then we are faced with pathological anxiety.
In most cases, such anxiety requires pharmacological help. Some of the symptoms that occur in pathological anxiety and that lorazepam manages to mitigate are:
- Palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea
- Headache and dizziness
- Restlessness, insecurity and fear of the future
- Insomnia
What family does it belong to?
Lorazepam is a drug that belongs to the benzodiazepine family. This group of drugs shares the same pharmacological action and can produce different actions:
- Anxiolytic
- Antiepileptic
- Hypnotic
- Muscle relaxant

The consumption of this group of drugs has increased notably in recent years in our country, with Spain being among the leading European countries. In addition, the drug most consumed as an anxiolytic would be lorazepam, as revealed by the AEMPS in its report on the use of anxiolytics and hypnotics between 2000-2012.
How does it work?
This anxiolytic acts by increasing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter responsible for reducing neuronal activity, especially in the limbic cortical system.
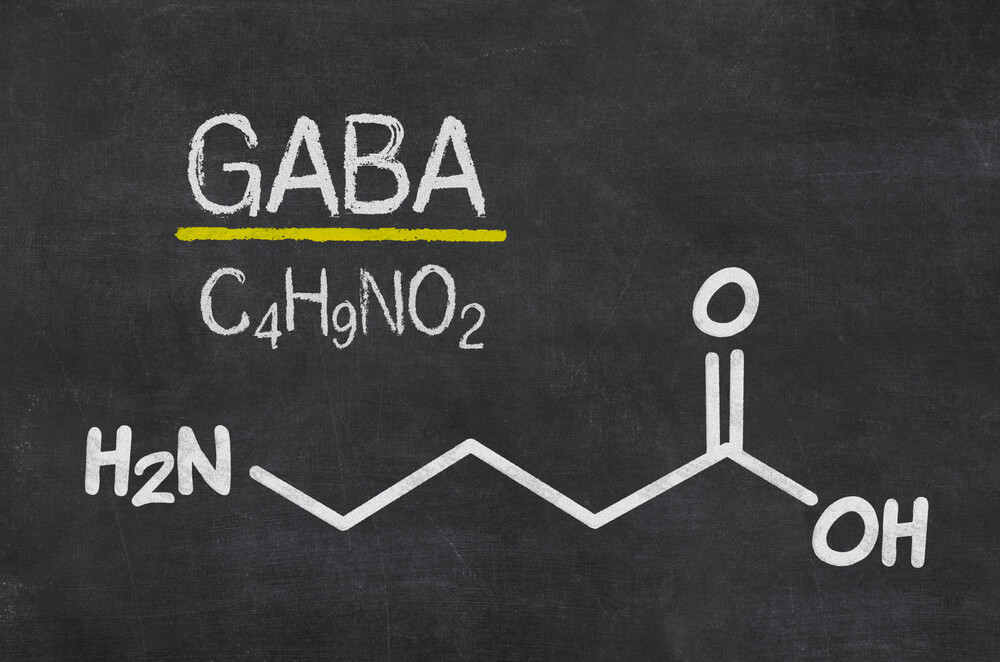
The increase in GABA activity occurs when lorazepam binds to the GABAergic receptor, causing said binding, in turn, an increase in the affinity between the neurotransmitter itself and its receptor. This last association between the two produces an increase in the concentration of chloride in the neuron, thus preventing its excitability.
You may be interested in: Alprazolam or Trankimazin, Facts and Curiosities
What are its pharmacokinetic properties?
Lorazepam, when administered orally, is absorbed in the digestive tract rapidly, with the first effects observed in the first 45 minutes. Generally, within two hours of its oral administration, the maximum concentration in the blood is reached.
Due to its high fat solubility, this drug can bind to proteins that circulate in the blood and cross the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from toxic substances.
It’s also capable of overcoming the placental barrier, being able to cause teratogenic effects during the first trimester or other problems in the neonate in subsequent trimesters. It’s also contraindicated during lactation, as lorazepam is excreted in breast milk.

In addition, during its hepatic metabolism, it doesn’t need to carry out the oxidation process, which makes it a recommended drug in older patients or those with liver problems.
Its elimination half-life, the time it takes to eliminate half of the drug, is 10 to 20 hours. This value brings us closer to the duration of the effects of lorazepam in the body.
Discover: The Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
What is the correct lorazepam dosage?
In cases of pathological anxiety, start with 0.5 milligrams divided into two or three doses a day. If necessary, the doctor will later prescribe an increase, but treatment should be started with the lowest dose. In the case of insomnia, the treatment is one milligram before going to bed, subsequently setting an increase if necessary.
During treatment, tolerance problems may occur, in which the drug loses efficacy, together with drug dependence problems, where withdrawal symptoms may appear after abrupt withdrawal of the drug. To prevent both problems, it’s important not to prolong the use of lorazepam without medical indication.
What are its main adverse reactions?

One in ten patients may experience drowsiness, a choking sensation, and sedation. The latter usually resolves in most cases in the first weeks, thanks to the acquired tolerance to the drug.
As a safety measure, in the face of such adverse reactions, you shouldn’t drive, at least until verifying that the drug doesn’t affect driving. Likewise, the consumption of alcohol and other CNS-depressant drugs should be avoided.
Lorazepam is also known by its trade name Orfidal. It’s a drug that’s considered to be psychotropic because it acts on the Central Nervous System (CNS). Their action can affect the consumer’s mood and behavior. At present, it’s one of the most consumed drugs in Europe.
What is lorazepam used for?
Lorazepam is a drug used primarily to reduce pathological anxiety. It can also be used in some cases for sleep disorders, such as insomnia, and for nervous and emotional disorders.
Anxiety is a vital defense mechanism of the body, which is triggered in the face of a threat, and which allows us to face it. But if this anxiety isn’t proportionate to the triggering threat, in duration or intensity, then we are faced with pathological anxiety.

In most cases, such anxiety requires pharmacological help. Some of the symptoms that occur in pathological anxiety and that lorazepam manages to mitigate are:
- Palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea
- Headache and dizziness
- Restlessness, insecurity and fear of the future
- Insomnia
What family does it belong to?
Lorazepam is a drug that belongs to the benzodiazepine family. This group of drugs shares the same pharmacological action and can produce different actions:
- Anxiolytic
- Antiepileptic
- Hypnotic
- Muscle relaxant

The consumption of this group of drugs has increased notably in recent years in our country, with Spain being among the leading European countries. In addition, the drug most consumed as an anxiolytic would be lorazepam, as revealed by the AEMPS in its report on the use of anxiolytics and hypnotics between 2000-2012.
How does it work?
This anxiolytic acts by increasing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter responsible for reducing neuronal activity, especially in the limbic cortical system.

The increase in GABA activity occurs when lorazepam binds to the GABAergic receptor, causing said binding, in turn, an increase in the affinity between the neurotransmitter itself and its receptor. This last association between the two produces an increase in the concentration of chloride in the neuron, thus preventing its excitability.
You may be interested in: Alprazolam or Trankimazin, Facts and Curiosities
What are its pharmacokinetic properties?
Lorazepam, when administered orally, is absorbed in the digestive tract rapidly, with the first effects observed in the first 45 minutes. Generally, within two hours of its oral administration, the maximum concentration in the blood is reached.
Due to its high fat solubility, this drug can bind to proteins that circulate in the blood and cross the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from toxic substances.
It’s also capable of overcoming the placental barrier, being able to cause teratogenic effects during the first trimester or other problems in the neonate in subsequent trimesters. It’s also contraindicated during lactation, as lorazepam is excreted in breast milk.

In addition, during its hepatic metabolism, it doesn’t need to carry out the oxidation process, which makes it a recommended drug in older patients or those with liver problems.
Its elimination half-life, the time it takes to eliminate half of the drug, is 10 to 20 hours. This value brings us closer to the duration of the effects of lorazepam in the body.
Discover: The Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
What is the correct lorazepam dosage?
In cases of pathological anxiety, start with 0.5 milligrams divided into two or three doses a day. If necessary, the doctor will later prescribe an increase, but treatment should be started with the lowest dose. In the case of insomnia, the treatment is one milligram before going to bed, subsequently setting an increase if necessary.
During treatment, tolerance problems may occur, in which the drug loses efficacy, together with drug dependence problems, where withdrawal symptoms may appear after abrupt withdrawal of the drug. To prevent both problems, it’s important not to prolong the use of lorazepam without medical indication.
What are its main adverse reactions?

One in ten patients may experience drowsiness, a choking sensation, and sedation. The latter usually resolves in most cases in the first weeks, thanks to the acquired tolerance to the drug.
As a safety measure, in the face of such adverse reactions, you shouldn’t drive, at least until verifying that the drug doesn’t affect driving. Likewise, the consumption of alcohol and other CNS-depressant drugs should be avoided.
- Informe utilización de medicamentos ansiolíticos e hipnóticos en España durante el periodo 2000-2012. Agencia Española del Medicamento. https://www.aemps.gob.es/medicamentosUsoHumano/observatorio/docs/ansioliticos_hipnoticos-2000-2012.pdf
- Vicens Pons, Eric. Ansiolíticos. Salud Mental De La Atención Primaria a la Comunitaria. Ágora Sanitaria 2018.
- Ficha técnica del Lorazepam Pensa. Agencia Española del Medicamento. http://cima.aemps.es/cima/pdfs/es/ft/68479/68479_ft.pdf
- Gómez Restrepo, Hernández Bayona, Rojas Urrego, Santacruz Oleas, Uribe Restrepo. Psiquiatría clínica, diagnóstico y tratamiento en niños, adolescentes y adultos. 3ª Ed. Médica Panamericana 2008; parte IV: 586-590.
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







