Simvastatin: Uses and Side Effects

Increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can have serious consequences for people’s health. Lifestyle changes and the use of certain drugs can bring these numbers back to normal. One of the drugs used for this purpose is simvastatin, but what are its side effects?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that the body synthesizes and that we can obtain from our food intake. It is used in the cell membrane and as a precursor of certain hormones. This substance is distributed in the bloodstream as high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
Various studies show that an increase in the intake of foods rich in fat and certain genetic mutations increase serum cholesterol levels. This increase can favor the appearance of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis.
What is simvastatin?
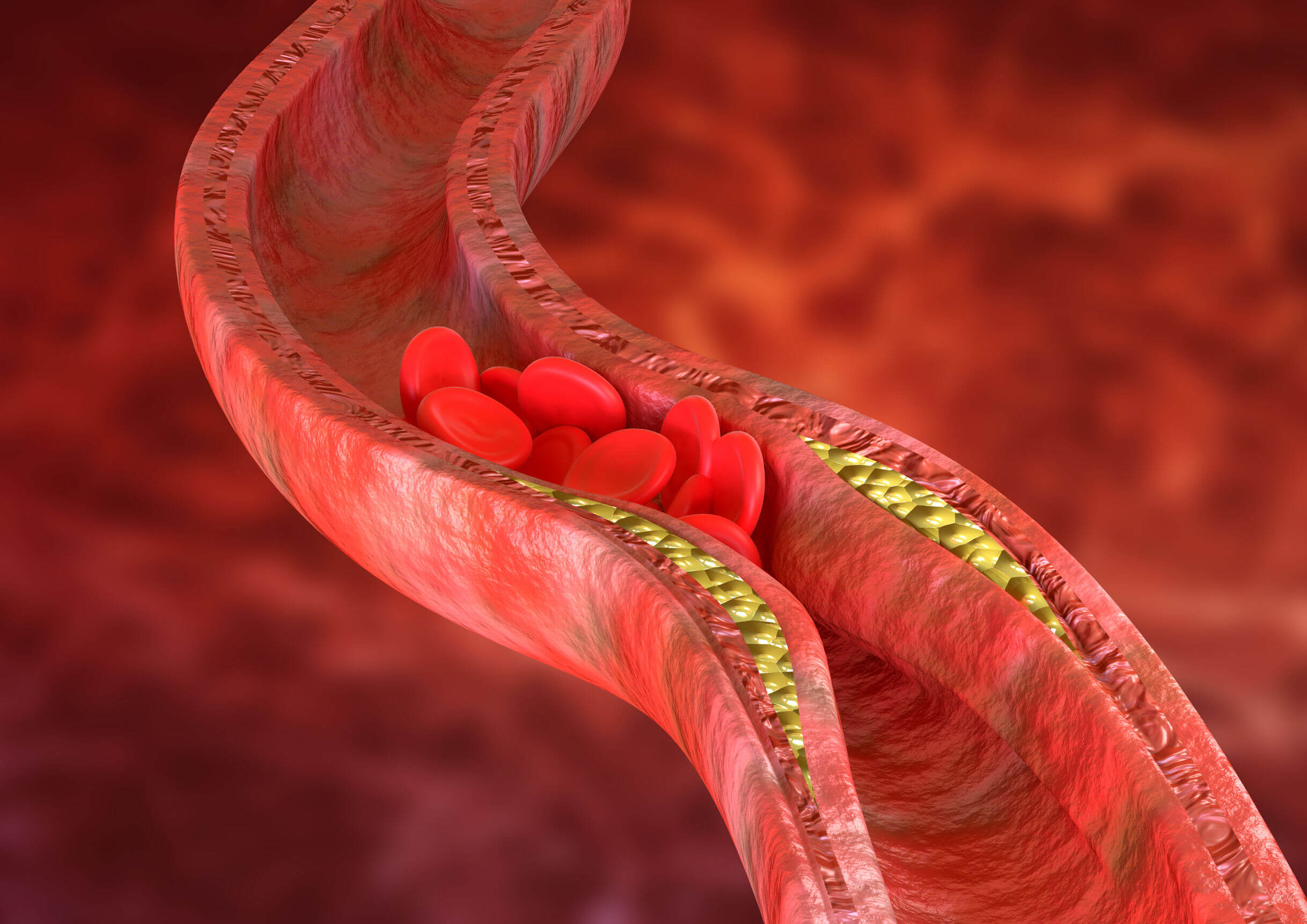
The drug in question is a drug derived from microbial products belonging to the group of statins. As with all drugs belonging to this group, the main function of simvastatin is to lower blood cholesterol levels, especially LDL.
Many people know LDL as the “bad cholesterol” because it’s the cholesterol that tends to accumulate on the walls of the blood vessels. Therefore, the compounds try to lower LDL levels and increase HDL levels, in order to favor the elimination of fatty compounds from the system.
Simvastatin is an effective drug that reaches its maximum blood concentration in as little as 2 hours. The ingestion of this compound must be done orally through film-coated tablets and can be found in presentations between 5 and 80 milligrams.
What’s it for?
As we’ve already said, simvastatin is used in patients with serum cholesterol levels above normal values. However, it’s only indicated in those cases where diet and lifestyle changes haven’t produced the desired effects.
In this sense, the drug is used in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia, as well as in people with mixed hyperlipidemia. Importantly, mixed hyperlipidemia is the increase in cholesterol and other fatty substances in the blood.
The use of statins can also help in the control of inherited diseases such as homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. In addition, it helps prolong life and prevent complications in people with coronary heart disease.
Mechanism of action of simvastatin
Simvastatin is a direct antagonist of the enzyme hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase. This means that it’s a drug that acts on the active site of the enzyme and blocks its action, preventing the transformation of HMG-CoA into mevalonate, thus limiting the synthesis of cholesterol.
This blockage triggers a series of biochemical activities whose purpose is to achieve a decrease in serum LDL levels. In turn, it also increases HDL levels to facilitate the excretion of cholesterol. Lastly, the enzymatic blockade also generates a decrease in intracellular isoprenoids, another intermediate in the synthesis of cholesterol.
In the case of children, studies show that the use of statins, in general, can cause a decrease in cholesterol levels of between 17 and 45%. However, this depends on the statin used and the dose administered.
How to take the drug?
This medicine to control cholesterol levels should be ingested whole, without crushing or chewing it and preferably with food. The ideal way is to consume the tablets during the night. However, it’s vitally important to consult with the doctor and follow the instructions that he offers.
According to the drug’s internal package insert, the recommended starting dose is between 10 and 40 milligrams. The dose can then be adjusted by the doctor as needed up to a maximum of 80 milligrams in a single dose overnight.
Your doctor may prescribe lower doses of simvastatin if you’re taking other drugs or if you have kidney disease.
Possible side effects of simvastatin

As with all commercialized drugs, simvastatin can cause some side effects in those who take it. However, these effects aren’t usually so intense and don’t limit the performance of other activities in most cases.
Among the most frequent adverse effects produced by the consumption of this cholesterol-lowering drug, the following stand out:
- Diarrhea
- Sickness
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Flatulence
- Headache
- Urticaria
Other more severe symptoms such as myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, and myositis may also appear, although their incidence is very low. However, it’s important to consult your doctor immediately when noticing any strange change in the state of health.
Warnings and contraindications
One of the main contraindications to the consumption of simvastatin is an allergy to the active ingredient or to any of the excipients of the compound. Allergic processes can manifest as inflammation of various areas of the body, fever, and difficulty breathing.
On the other hand, it’s also contraindicated in patients with liver failure or with active liver disease such as hepatitis. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding shouldn’t take this drug, as it can have negative effects on the baby’s health.
Simvastatin is capable of increasing the effect of anticoagulant drugs in the body, and so its simultaneous consumption isn’t recommended. In addition, neither is it recommended to take this medicine together with immunosuppressants as it increases the risk of rhabdomyolysis.
Lastly, the compound should be used with caution in people with a history of allergies to other statins, active alcoholism, a history of liver disease, or organ transplantation.
Treatment should be supported by changes in diet
The drug in question is used to reduce serum cholesterol levels in different pathologies. It exerts its action by blocking an enzyme and limiting cholesterol biosynthesis. However, for best results, its use should be accompanied by changes in diet and lifestyle.
Consumption of simvastatin is safe in most cases, although there’s the possibility of developing severe side effects such as rhabdomyolysis. In this sense, it’s very important to follow the instructions provided by the specialist and consult any questions you may have before starting treatment.
Increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can have serious consequences for people’s health. Lifestyle changes and the use of certain drugs can bring these numbers back to normal. One of the drugs used for this purpose is simvastatin, but what are its side effects?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that the body synthesizes and that we can obtain from our food intake. It is used in the cell membrane and as a precursor of certain hormones. This substance is distributed in the bloodstream as high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
Various studies show that an increase in the intake of foods rich in fat and certain genetic mutations increase serum cholesterol levels. This increase can favor the appearance of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis.
What is simvastatin?

The drug in question is a drug derived from microbial products belonging to the group of statins. As with all drugs belonging to this group, the main function of simvastatin is to lower blood cholesterol levels, especially LDL.
Many people know LDL as the “bad cholesterol” because it’s the cholesterol that tends to accumulate on the walls of the blood vessels. Therefore, the compounds try to lower LDL levels and increase HDL levels, in order to favor the elimination of fatty compounds from the system.
Simvastatin is an effective drug that reaches its maximum blood concentration in as little as 2 hours. The ingestion of this compound must be done orally through film-coated tablets and can be found in presentations between 5 and 80 milligrams.
What’s it for?
As we’ve already said, simvastatin is used in patients with serum cholesterol levels above normal values. However, it’s only indicated in those cases where diet and lifestyle changes haven’t produced the desired effects.
In this sense, the drug is used in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia, as well as in people with mixed hyperlipidemia. Importantly, mixed hyperlipidemia is the increase in cholesterol and other fatty substances in the blood.
The use of statins can also help in the control of inherited diseases such as homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. In addition, it helps prolong life and prevent complications in people with coronary heart disease.
Mechanism of action of simvastatin
Simvastatin is a direct antagonist of the enzyme hydroxy-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase. This means that it’s a drug that acts on the active site of the enzyme and blocks its action, preventing the transformation of HMG-CoA into mevalonate, thus limiting the synthesis of cholesterol.
This blockage triggers a series of biochemical activities whose purpose is to achieve a decrease in serum LDL levels. In turn, it also increases HDL levels to facilitate the excretion of cholesterol. Lastly, the enzymatic blockade also generates a decrease in intracellular isoprenoids, another intermediate in the synthesis of cholesterol.
In the case of children, studies show that the use of statins, in general, can cause a decrease in cholesterol levels of between 17 and 45%. However, this depends on the statin used and the dose administered.
How to take the drug?
This medicine to control cholesterol levels should be ingested whole, without crushing or chewing it and preferably with food. The ideal way is to consume the tablets during the night. However, it’s vitally important to consult with the doctor and follow the instructions that he offers.
According to the drug’s internal package insert, the recommended starting dose is between 10 and 40 milligrams. The dose can then be adjusted by the doctor as needed up to a maximum of 80 milligrams in a single dose overnight.
Your doctor may prescribe lower doses of simvastatin if you’re taking other drugs or if you have kidney disease.
Possible side effects of simvastatin

As with all commercialized drugs, simvastatin can cause some side effects in those who take it. However, these effects aren’t usually so intense and don’t limit the performance of other activities in most cases.
Among the most frequent adverse effects produced by the consumption of this cholesterol-lowering drug, the following stand out:
- Diarrhea
- Sickness
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Flatulence
- Headache
- Urticaria
Other more severe symptoms such as myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, and myositis may also appear, although their incidence is very low. However, it’s important to consult your doctor immediately when noticing any strange change in the state of health.
Warnings and contraindications
One of the main contraindications to the consumption of simvastatin is an allergy to the active ingredient or to any of the excipients of the compound. Allergic processes can manifest as inflammation of various areas of the body, fever, and difficulty breathing.
On the other hand, it’s also contraindicated in patients with liver failure or with active liver disease such as hepatitis. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding shouldn’t take this drug, as it can have negative effects on the baby’s health.
Simvastatin is capable of increasing the effect of anticoagulant drugs in the body, and so its simultaneous consumption isn’t recommended. In addition, neither is it recommended to take this medicine together with immunosuppressants as it increases the risk of rhabdomyolysis.
Lastly, the compound should be used with caution in people with a history of allergies to other statins, active alcoholism, a history of liver disease, or organ transplantation.
Treatment should be supported by changes in diet
The drug in question is used to reduce serum cholesterol levels in different pathologies. It exerts its action by blocking an enzyme and limiting cholesterol biosynthesis. However, for best results, its use should be accompanied by changes in diet and lifestyle.
Consumption of simvastatin is safe in most cases, although there’s the possibility of developing severe side effects such as rhabdomyolysis. In this sense, it’s very important to follow the instructions provided by the specialist and consult any questions you may have before starting treatment.
- Maldonado Saavedra O, Ramírez Sánchez I, García Sánchez J, Ceballos Reyes G, Méndez Bolaina E. Colesterol: Función biológica e implicaciones médicas. Rev. mex. cienc. farm. 2012; 43( 2 ): 7-22.
- González Jiménez E, Álvarez Ferre J. Estatinas: Características y Efectos sobre el Control Lipídico en el Niño y Adolescente Obeso. Rev Clin Med Fam. 2011; 4( 1 ): 69-75.
- Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios. Prospecto: Simvastatina Pensa 20 mg comprimidos recubiertos con película EFG. Documento disponible en: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/p/65880/Prospecto_65880.html#introducci-n
- Cejka J, Kratochvíl B, Císarová I, Jegorov A. Simvastatin. Acta Crystallogr C. 2003 Aug;59(Pt 8):o428-30.
- Pedersen TR, Tobert JA. Simvastatin: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Dec;5(12):2583-96.
- de Faria CA, Zanette DL, Silva WA Jr, Ribeiro-Paes JT. PAI-1 inhibition by simvastatin as a positive adjuvant in cell therapy. Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1511-1517.
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







