What Is Fibromyalgia?

Fibromyalgia is a chronic disease characterized by widespread moderate to severe musculoskeletal pain.
The patients suffer from exaggerated hypersensitivity in many parts of the body without demonstrable organic alterations.
The word fibromyalgia means pain in the muscles and fibrous tissue. It’s a common disease, and between 2 and 6% of the population suffers from it, with women being the more likely to suffer from it.
It’s observed mainly between 20 and 50 years of age, although there are cases of children and the elderly suffering from this disease too.
It can appear on its own, and, in this case, we speak of primary fibromyalgia, or it can also be associated with other diseases (concomitant fibromyalgia).
Causes of fibromyalgia
The exact cause of this disease isn’t known, and experts think that there are many factors involved.
Some people develop the disease without any apparent cause. However, in others, it begins after identifiable processes such as a bacterial and viral infection, a car accident, or after other diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus erythematosus, among others.
However, these agents don’t seem to be responsible for the development of fibromyalgia, but what they probably do is awaken it in a person who has a hidden abnormality in the regulation of their ability to respond to certain stimuli.
Its regulation has been observed with disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system, alterations in neurotransmitters and hormones, sleep disturbances, and genetic factors, among others.
Symptoms

The central symptom is generalized pain in muscles, joints and ligaments, accompanied by:
- Severe fatigue and muscle stiffness: they usually appear in the morning and get worse with rest.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Memory loss and trouble concentrating.
- Headaches
- Anxiety and sadness that derive from the ability to lead a normal life.
Although the pain is constant, fibromyalgia symptoms emerge as flare-ups. The patient goes through phases of stability and others in which they worsen.
Each person evolves in a different way. Therefore, it’s difficult to define the causes of fibromyalgia and a single treatment that works in all cases. Also, a person can suffer from two chronic pain-related diseases at the same time.
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, the patient has other problems such as:
- Skin problems
- Chest symptoms
- Vertigo and imbalance problems
- Others
You may be interested in: How to Diagnose Fibromyalgia
How is it treated?

There’s no treatment that will cure the disease in its entirety. However, there is treatment to help improve quality of life without having such frequent pain crises.
It’s important to know the nature of the disease and the triggers of the outbreaks, and to establish the best conditions for a restful sleep.
Fibromyalgia treatment should be guided by a rheumatologist, a physical therapist and, where necessary, a psychiatrist. It generally includes:
Medication for pain and depression
To relieve pain in the body, the doctor may recommend taking pain relievers and anti-inflammatories such as tramadol. However, these drugs aren’t always effective and the doctor can switch the medication to others that act on the central nervous system.
In cases where the patient suffers from anxiety, depression, and sleep problems, the specialist may prescribe drugs to combat these problems. In fact, these comorbidities often greatly reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Discover: Acupuncture for Fibromyalgia: What Does Science Say?
Physiotherapy
To improve movements, physiotherapy sessions are recommended. To be effective, they must be performed at least twice a week.
The physiotherapist will do therapeutic massages, stretching, and relaxation exercises, as this helps reduce symptoms by promoting local analgesia and improving blood circulation.
Doing physical activity
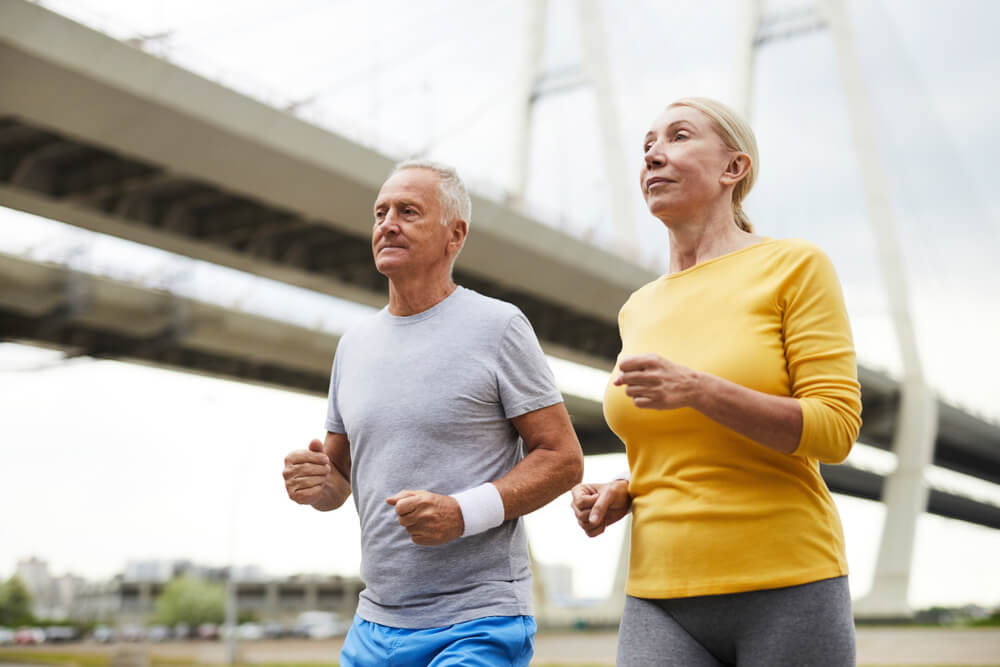

This is another important measure to improve quality of life in fibromyalgia patients. However, you should follow the instructions of the doctor and the physical trainer to perform exercises that help relieve pain and stretch the muscles.
Some of these exercises include walking, swimming, and water gymnastics. They’re usually done 3 to 5 times a week for 30 to 60 minutes.
Evolution
Despite being a benign disease (it doesn’t produce physical sequelae, nor does it influence the survival of the patient) the impact it causes on the person’s quality of life is highly variable from one person to another. It can limit people to different degrees and different lengths of time.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disease characterized by widespread moderate to severe musculoskeletal pain.
The patients suffer from exaggerated hypersensitivity in many parts of the body without demonstrable organic alterations.
The word fibromyalgia means pain in the muscles and fibrous tissue. It’s a common disease, and between 2 and 6% of the population suffers from it, with women being the more likely to suffer from it.
It’s observed mainly between 20 and 50 years of age, although there are cases of children and the elderly suffering from this disease too.
It can appear on its own, and, in this case, we speak of primary fibromyalgia, or it can also be associated with other diseases (concomitant fibromyalgia).
Causes of fibromyalgia

The exact cause of this disease isn’t known, and experts think that there are many factors involved.
Some people develop the disease without any apparent cause. However, in others, it begins after identifiable processes such as a bacterial and viral infection, a car accident, or after other diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus erythematosus, among others.
However, these agents don’t seem to be responsible for the development of fibromyalgia, but what they probably do is awaken it in a person who has a hidden abnormality in the regulation of their ability to respond to certain stimuli.
Its regulation has been observed with disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system, alterations in neurotransmitters and hormones, sleep disturbances, and genetic factors, among others.
Symptoms

The central symptom is generalized pain in muscles, joints and ligaments, accompanied by:
- Severe fatigue and muscle stiffness: they usually appear in the morning and get worse with rest.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Memory loss and trouble concentrating.
- Headaches
- Anxiety and sadness that derive from the ability to lead a normal life.
Although the pain is constant, fibromyalgia symptoms emerge as flare-ups. The patient goes through phases of stability and others in which they worsen.
Each person evolves in a different way. Therefore, it’s difficult to define the causes of fibromyalgia and a single treatment that works in all cases. Also, a person can suffer from two chronic pain-related diseases at the same time.
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, the patient has other problems such as:
- Skin problems
- Chest symptoms
- Vertigo and imbalance problems
- Others
You may be interested in: How to Diagnose Fibromyalgia
How is it treated?

There’s no treatment that will cure the disease in its entirety. However, there is treatment to help improve quality of life without having such frequent pain crises.
It’s important to know the nature of the disease and the triggers of the outbreaks, and to establish the best conditions for a restful sleep.
Fibromyalgia treatment should be guided by a rheumatologist, a physical therapist and, where necessary, a psychiatrist. It generally includes:
Medication for pain and depression
To relieve pain in the body, the doctor may recommend taking pain relievers and anti-inflammatories such as tramadol. However, these drugs aren’t always effective and the doctor can switch the medication to others that act on the central nervous system.
In cases where the patient suffers from anxiety, depression, and sleep problems, the specialist may prescribe drugs to combat these problems. In fact, these comorbidities often greatly reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Discover: Acupuncture for Fibromyalgia: What Does Science Say?
Physiotherapy
To improve movements, physiotherapy sessions are recommended. To be effective, they must be performed at least twice a week.
The physiotherapist will do therapeutic massages, stretching, and relaxation exercises, as this helps reduce symptoms by promoting local analgesia and improving blood circulation.
Doing physical activity

This is another important measure to improve quality of life in fibromyalgia patients. However, you should follow the instructions of the doctor and the physical trainer to perform exercises that help relieve pain and stretch the muscles.
Some of these exercises include walking, swimming, and water gymnastics. They’re usually done 3 to 5 times a week for 30 to 60 minutes.
Evolution
Despite being a benign disease (it doesn’t produce physical sequelae, nor does it influence the survival of the patient) the impact it causes on the person’s quality of life is highly variable from one person to another. It can limit people to different degrees and different lengths of time.
- Sifuentes-Giraldo, W. A., & Morell-Hita, J. L. (2017). Fibromialgia. Medicine (Spain). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.med.2017.02.004
- Prados, G., & Miró, E. (2012). Fibromialgia y sueño: Una revisión. Revista de Neurologia.
- de Vicente, A., Magán, I., & Berdullas, S. (2009). La fibromialgia. Infocop. https://doi.org/10.4321/S0211-57352004000100008
- Secretaría de Gobernación. (2016). ¿Qué es la fibromialgia? Enlace. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2006.355136
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







