Vitamin B12 Deficiency: What Are its Consequences?


Escrito y verificado por el nutricionista Saúl Sánchez
Vitamin B12 belongs to the group of water-soluble vitamins. We can find it in foods of animal origin and a continuous supply of it is needed to avoid a deficit. In this article, we’re going to explain all you need to know about this nutrient, which is so important for a healthy life.
The first thing we need to be clear about is that there are certain restrictive diets, such as vegan, that don’t include foods of animal origin in their spectrum. This generates a negative impact on the levels of vitamin B12, making its supplementation essential in order to prevent major problems.
Functions of vitamin B12
The main function of vitamin B12 is to participate in the synthesis of red blood cells, as stated in a study published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition. For this reason, a lack of it can condition malformations in these cells, which is related to health problems that we will look at later.
In parallel, this micronutrient also acts in different metabolic pathways related to proteins. In addition, it ensures the proper functioning of the central nervous system, according to the most recent scientific literature.
How to achieve a correct contribution of the substance?
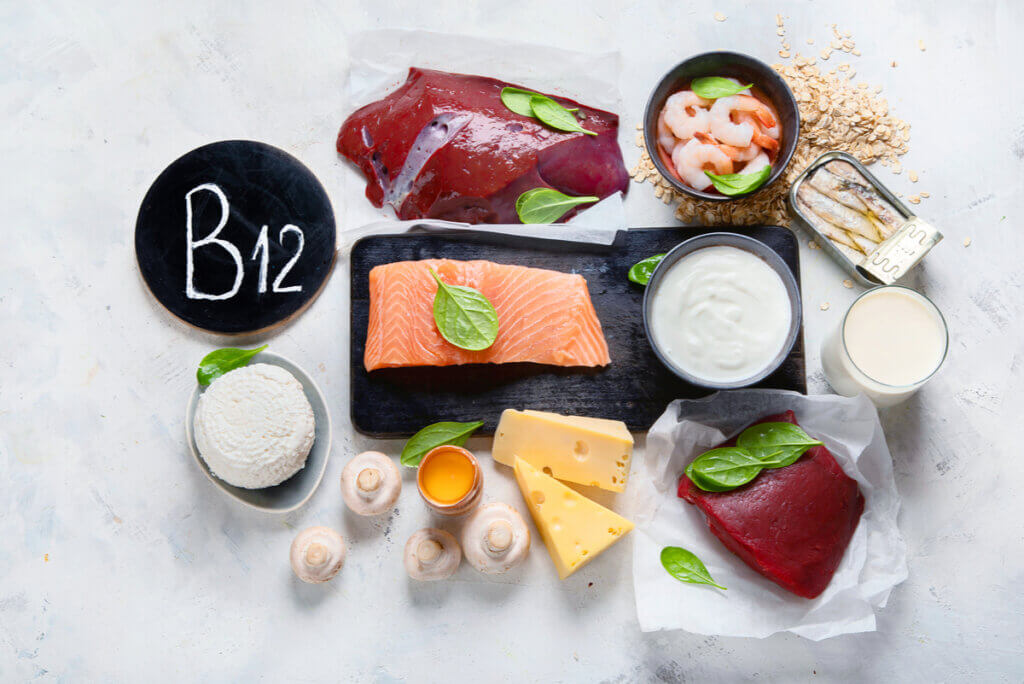
As we have stated, vitamin B12 is found in foods of animal origin. Meats, eggs, and dairy are sources of this nutrient, and so a varied diet should ensure that the requirements are met, thus avoiding major complications.
However, the problem comes when we talk about restrictive diets. The vegan diet, for example, doesn’t have food in its spectrum that contains the micronutrient, and so it’s necessary to include a supplement of this vitamin.
Under normal conditions, and assuming a healthy and varied diet, a deficiency in vitamin B12 is rare. We normally have a sufficient daily intake of it with a balanced diet, and, even though there are no significant deposits in the body, due to its water-soluble nature, the symptoms of its deficiency take time to manifest.
The consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency
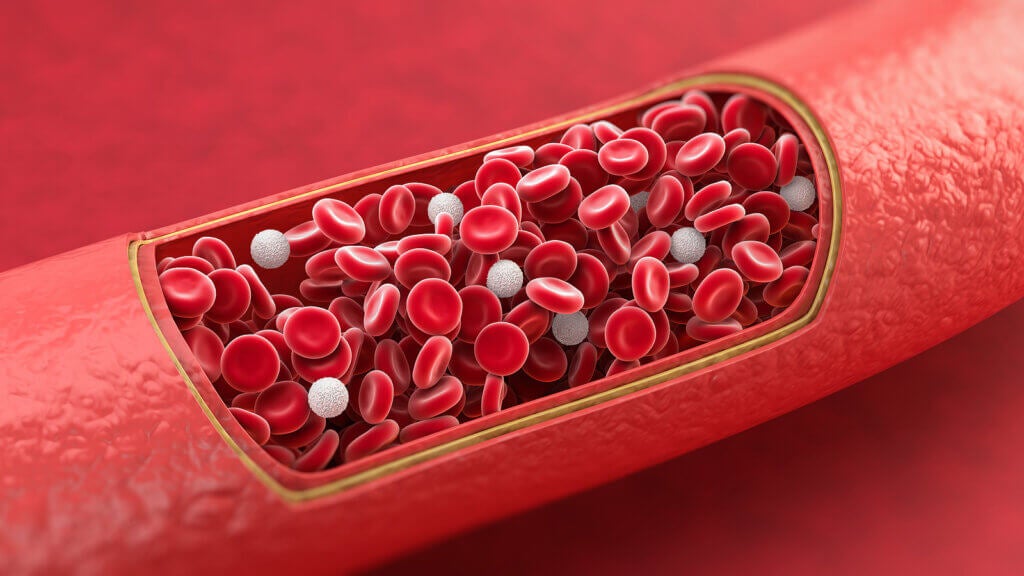
The first of the consequences of a lack of vitamin B12 in the diet is the appearance of megaloblastic anemia. This is evidenced by current research. This is a defect that occurs in the production of red blood cells that makes them inefficient in transporting oxygen.
The main symptom of this type of anemia is tiredness. The blood reduces its oxygen content and this element reaches the cells to a lesser degree. Taking into account that many physiological and metabolic pathways are dependent on this molecule, its efficiency is conditioned. For this reason, it isn’t surprising that this will create a situation of chronic fatigue.
In addition, other problems may arise from a poor intake of the nutrient. Recent studies link a low level of vitamin B12 with an increase in the development of cardiovascular diseases, especially in the context of the elderly. An inefficient supply of the micronutrient could cause an increase in the concentration of homocysteine, a substance associated with an increased cardiac risk.
Finally, it should be noted that a deficiency of it generates problems related to cognition. Central nervous system symptoms have been associated with pediatric patients who experience an inadequate supply of the nutrient.
What to do in the case of a vitamin B12 deficiency?
If you experience fatigue or tiredness and you can’t find a clear explanation for this situation, it’s advisable that you go to a specialist to assess the situation. The doctor may request an analysis that shows the values of vitamin B12, iron, and the most influential hormones.
The common thing is for a doctor to prescribes a vitamin B12 supplement to correct the deficiency that has been created. However, this is only equivalent to applying a small patch to the problem. The best thing to do here is to acquire the services of an expert in nutrition who will assess your normal diet and detect possible inefficiencies in its intake of nutrients, and, in this case, vitamin B12.
In this way, if you carry out a restrictive diet, it will be necessary to establish which dietary supplements you should take regularly and in what doses. If the diet is varied, then it may be necessary to regularly introduce foods with a high density, such as red meat or organ meats.
Other causes of anemia
The feeling of fatigue and chronic tiredness can be the warning sign that there is a process of anemia. However, the cause doesn’t always have to be a deficiency of vitamin B12. It’s even more frequent that the origin of the problem is actually an inefficient supply of iron.
For this reason, if iron deficiency anemia is detected, the most effective solution is usually the administration and prescription of artificial iron and the modification of dietary habits. With regard to anemia in general, the most appropriate solution here is prevention, as once the pathology has developed, improvement occurs slowly.
Excess vitamin B12 and its problems
Just as a deficiency of vitamin B12 is considered harmful to health, an excess of it can also be counterproductive. Some research published in 2019 has linked the excessive and chronic intake of the vitamin with an increased risk of developing lung cancer.
It is clear that the results can’t yet provide any conclusive evidence. However, several articles suggest that too high an intake of B vitamins can be harmful to the functioning of various systems. This is even the case from a cardiovascular point of view.
For this reason, supplementation shouldn’t be prescribed by default to the general population. The best way forward is to analyze each case individually and always try to introduce the nutrient through food. Only if this isn’t possible should you assess the possibility of using a supplement to prevent this deficit.
You need to be careful with multivitamins. These products usually have megadoses of some micronutrients that, when administered in a sustained way, don’t work well with the body and its metabolism. There are even cases of some that are enriched with caffeine, which could generate a tolerance to the substance.

The importance of a varied diet
In order to prevent the development of pathologies derived from the deficit or overdose of certain nutrients, the most appropriate way forward is to ensure you have a varied diet. Products from all groups must be included in the usual diet, and efforts made to reduce restrictions.
Likewise, it’s advisable to avoid elements that have been shown to be toxic in any quantity. We’re talking here about alcohol and tobacco, as well as certain additives that are hidden in ultra-processed products. Nitrites that are used as preservatives could be a clear example of this.
At the same time, regular exercise is recommended. Physical activity improves the functioning of the metabolism and the physiological reactions that constantly take place in the human body. Remember that a sedentary lifestyle is one of the most frequent risk factors.
Vitamin B12: an essential nutrient
Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that can’t be manufactured endogenously in the human body, and for this reason it must be provided through the diet. However, as we’ve mentioned, we only find it in animal products. Restrictive eating plans can be deficient in this element.
In the case of detecting an inefficient intake of this vitamin, it may be appropriate to propose vitamin supplements, although this must never be chronically extended over time. The main source should always be your intake through food, in order to guarantee a correct and natural consumption.
Keep in mind that the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency are never immediate, but can occur in the medium term or on a gradual basis. In this way, if you experience fatigue or chronic fatigue, then go to the specialist for an assessment test. The blood test is usually the best diagnostic tool in these cases.
We also recommend that you visit the nutritionist in order to provide dietary guidelines and prevent this situation from occurring again in the future. In this way, you’ll improve your overall health and help to prevent complex pathologies.
Vitamin B12 belongs to the group of water-soluble vitamins. We can find it in foods of animal origin and a continuous supply of it is needed to avoid a deficit. In this article, we’re going to explain all you need to know about this nutrient, which is so important for a healthy life.
The first thing we need to be clear about is that there are certain restrictive diets, such as vegan, that don’t include foods of animal origin in their spectrum. This generates a negative impact on the levels of vitamin B12, making its supplementation essential in order to prevent major problems.
Functions of vitamin B12
The main function of vitamin B12 is to participate in the synthesis of red blood cells, as stated in a study published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition. For this reason, a lack of it can condition malformations in these cells, which is related to health problems that we will look at later.
In parallel, this micronutrient also acts in different metabolic pathways related to proteins. In addition, it ensures the proper functioning of the central nervous system, according to the most recent scientific literature.
How to achieve a correct contribution of the substance?
As we have stated, vitamin B12 is found in foods of animal origin. Meats, eggs, and dairy are sources of this nutrient, and so a varied diet should ensure that the requirements are met, thus avoiding major complications.
However, the problem comes when we talk about restrictive diets. The vegan diet, for example, doesn’t have food in its spectrum that contains the micronutrient, and so it’s necessary to include a supplement of this vitamin.
Under normal conditions, and assuming a healthy and varied diet, a deficiency in vitamin B12 is rare. We normally have a sufficient daily intake of it with a balanced diet, and, even though there are no significant deposits in the body, due to its water-soluble nature, the symptoms of its deficiency take time to manifest.

The consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency
The first of the consequences of a lack of vitamin B12 in the diet is the appearance of megaloblastic anemia. This is evidenced by current research. This is a defect that occurs in the production of red blood cells that makes them inefficient in transporting oxygen.
The main symptom of this type of anemia is tiredness. The blood reduces its oxygen content and this element reaches the cells to a lesser degree. Taking into account that many physiological and metabolic pathways are dependent on this molecule, its efficiency is conditioned. For this reason, it isn’t surprising that this will create a situation of chronic fatigue.
In addition, other problems may arise from a poor intake of the nutrient. Recent studies link a low level of vitamin B12 with an increase in the development of cardiovascular diseases, especially in the context of the elderly. An inefficient supply of the micronutrient could cause an increase in the concentration of homocysteine, a substance associated with an increased cardiac risk.
Finally, it should be noted that a deficiency of it generates problems related to cognition. Central nervous system symptoms have been associated with pediatric patients who experience an inadequate supply of the nutrient.
What to do in the case of a vitamin B12 deficiency?
If you experience fatigue or tiredness and you can’t find a clear explanation for this situation, it’s advisable that you go to a specialist to assess the situation. The doctor may request an analysis that shows the values of vitamin B12, iron, and the most influential hormones.
The common thing is for a doctor to prescribes a vitamin B12 supplement to correct the deficiency that has been created. However, this is only equivalent to applying a small patch to the problem. The best thing to do here is to acquire the services of an expert in nutrition who will assess your normal diet and detect possible inefficiencies in its intake of nutrients, and, in this case, vitamin B12.
In this way, if you carry out a restrictive diet, it will be necessary to establish which dietary supplements you should take regularly and in what doses. If the diet is varied, then it may be necessary to regularly introduce foods with a high density, such as red meat or organ meats.
Other causes of anemia
The feeling of fatigue and chronic tiredness can be the warning sign that there is a process of anemia. However, the cause doesn’t always have to be a deficiency of vitamin B12. It’s even more frequent that the origin of the problem is actually an inefficient supply of iron.
For this reason, if iron deficiency anemia is detected, the most effective solution is usually the administration and prescription of artificial iron and the modification of dietary habits. With regard to anemia in general, the most appropriate solution here is prevention, as once the pathology has developed, improvement occurs slowly.
Excess vitamin B12 and its problems
Just as a deficiency of vitamin B12 is considered harmful to health, an excess of it can also be counterproductive. Some research published in 2019 has linked the excessive and chronic intake of the vitamin with an increased risk of developing lung cancer.
It is clear that the results can’t yet provide any conclusive evidence. However, several articles suggest that too high an intake of B vitamins can be harmful to the functioning of various systems. This is even the case from a cardiovascular point of view.
For this reason, supplementation shouldn’t be prescribed by default to the general population. The best way forward is to analyze each case individually and always try to introduce the nutrient through food. Only if this isn’t possible should you assess the possibility of using a supplement to prevent this deficit.
You need to be careful with multivitamins. These products usually have megadoses of some micronutrients that, when administered in a sustained way, don’t work well with the body and its metabolism. There are even cases of some that are enriched with caffeine, which could generate a tolerance to the substance.

The importance of a varied diet
In order to prevent the development of pathologies derived from the deficit or overdose of certain nutrients, the most appropriate way forward is to ensure you have a varied diet. Products from all groups must be included in the usual diet, and efforts made to reduce restrictions.
Likewise, it’s advisable to avoid elements that have been shown to be toxic in any quantity. We’re talking here about alcohol and tobacco, as well as certain additives that are hidden in ultra-processed products. Nitrites that are used as preservatives could be a clear example of this.
At the same time, regular exercise is recommended. Physical activity improves the functioning of the metabolism and the physiological reactions that constantly take place in the human body. Remember that a sedentary lifestyle is one of the most frequent risk factors.
Vitamin B12: an essential nutrient
Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that can’t be manufactured endogenously in the human body, and for this reason it must be provided through the diet. However, as we’ve mentioned, we only find it in animal products. Restrictive eating plans can be deficient in this element.
In the case of detecting an inefficient intake of this vitamin, it may be appropriate to propose vitamin supplements, although this must never be chronically extended over time. The main source should always be your intake through food, in order to guarantee a correct and natural consumption.
Keep in mind that the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency are never immediate, but can occur in the medium term or on a gradual basis. In this way, if you experience fatigue or chronic fatigue, then go to the specialist for an assessment test. The blood test is usually the best diagnostic tool in these cases.
We also recommend that you visit the nutritionist in order to provide dietary guidelines and prevent this situation from occurring again in the future. In this way, you’ll improve your overall health and help to prevent complex pathologies.
- Obeid R., Heil SG., Verhoeven MA., Heuvel EG., et al., Vitamin B12 intake from animal foods, biomarkers, and health aspects. Front Nutr, 2019.
- Pavlov CS., Damulin IV., Shulpekova YO., Andreev EA., Neurological disorders in vitamin B12 deficiency. Ter Arkh, 2019. 91 (4): 122-129.
- Rivera-Rodríguez, Krystal M., and Raúl H. Morales-Borges. “¿ Están asociados los niveles altos de B12 con el cáncer?.” INDEX: 39.
- Langan RC., Goodbred AJ., Vitamin B12 deficiency: recognition and management. Am Fam Physician, 2017. 96 (6): 384-389.
- Spence JD., Metabolic vitamin B12 deficiency: a missed opportuinty to prevent dementia and stroke. Nutr Res, 2016. 36 (2): 109-16.
- Serin HM., Arslan EA., Neurological symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency: analysis of pediatric patients. Acta Clin Croat, 2019. 58 (2): 295-302.
- Fanidi A., Carreras Torres R., Larose TL., Yuan JM., et al., Is high vitamin B12 status a cause of lung cancer? Int J Cancer, 2019. 145 (6): 1499-1503.
Este texto se ofrece únicamente con propósitos informativos y no reemplaza la consulta con un profesional. Ante dudas, consulta a tu especialista.







